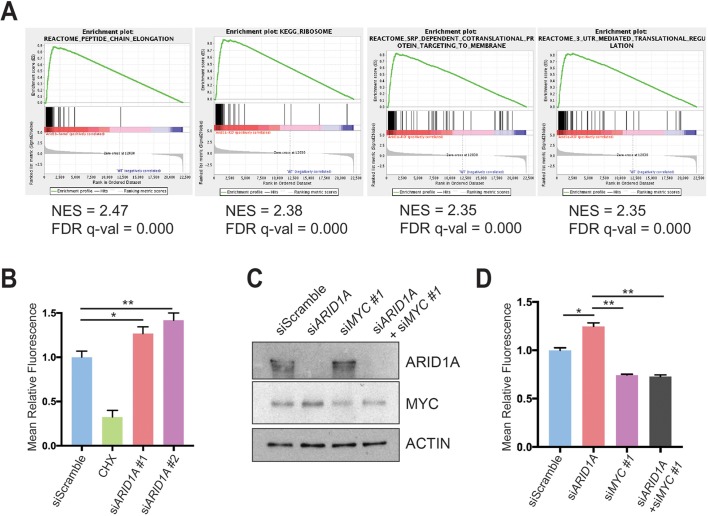
Figure 6.
ARID1A loss induces MYC-mediated increase in protein synthesis. (A) Gene set enrichment analysis of RNA-seq of Ptf1a-Cre; Arid1af/f (CA) mice pancreata using the ‘Molecular Signatures Database’ demonstrated that the top four upregulated signatures in CA mice were associated with protein translation. NES, normalised enrichment score; FDR, false discovery rate. (B) Human pancreatic ductal epithelial (HPDE) cells were treated with O-propargyl-puromycin (OPP), which were incorporated into nascent peptides, labelled with fluorescence and quantified with fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS). Representative FACS plot (left) and quantification (right) are shown. HPDE cells were treated siScramble (n=7), siARID1A 1 (n=6) and siARID1A 2 (n=6). Cycloheximide (CHX) is a translation inhibitor and served as a negative control for the assay in cells treated with siScramble (n=2). *P<0.05, **P<0.01. (C) Western blot demonstrating partial knockdown of MYC with siMYC in HPDE cells. (D) HPDE cells were treated with OPP and treated with siScramble (n=8), siARID1A (n=3), siMYC 1 (n=7) and siARID1A and siMYC 1 (n=3). Quantification of relative fluorescence is shown. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.