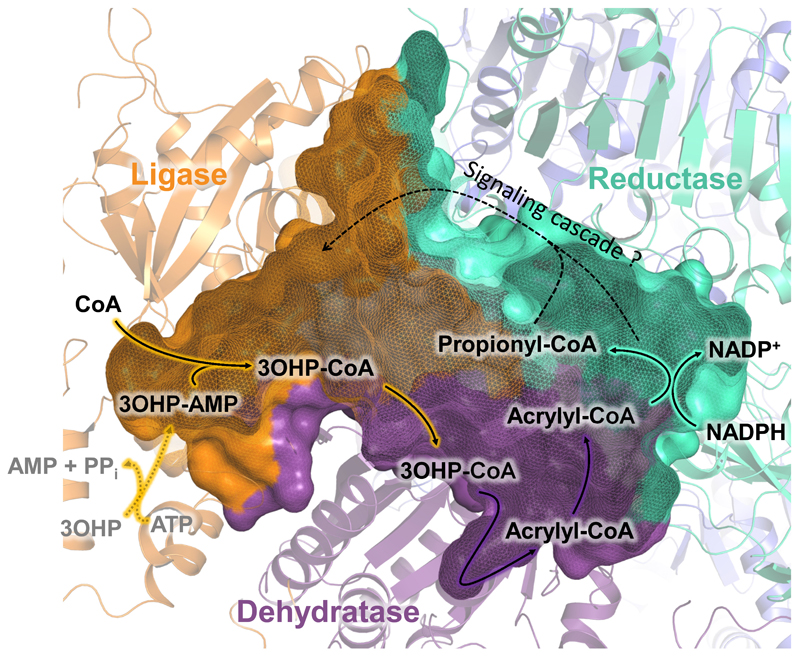
Figure 4. Proposed catalytic cycle of PCS.
In the open conformation, 3-hydroxypropionate (3OHP) and ATP are converted to 3-hydroxypropionyl-AMP (3OHP-AMP) through the ligase domain (orange). The binding of CoA induces closing of the enzyme and the formation of 3-hydroxypropionyl-CoA (3OHP-CoA). 3OHP-CoA is released into the reaction chamber, where it is converted by the dehydratase domain (purple) to acrylyl-CoA. Acrylyl-CoA then enters the active site of the reductase domain (cyan). Following the reduction of acrylyl-CoA to propionyl-CoA, the reaction chamber reopens to release propionyl-CoA, which leaves PCS ready for the next catalytic cycle.