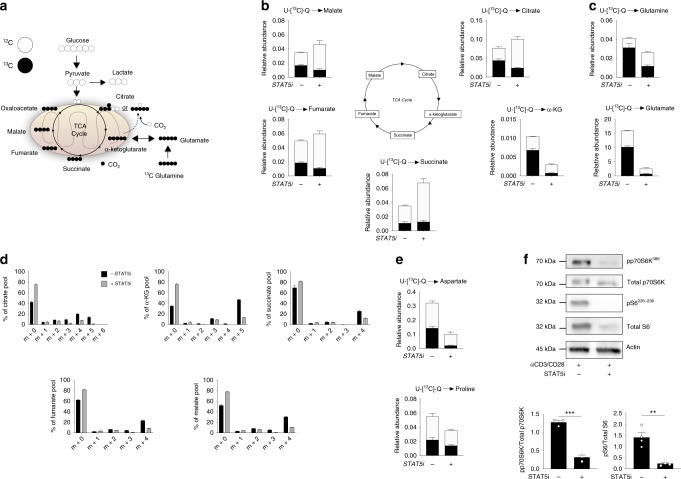
Fig. 6.
STAT5 regulates glutaminolysis in an mTORC1-dependent manner. a Schematic summarising incorporation of uniformly labelled 13C-glutamine into the TCA cycle. NV T-cells were activated (anti-CD3/CD28) in the presence or absence of STAT5i (100 μM) for 4 h. b Relative abundance of glutamine-derived 12C and 13C TCA cycle metabolites, citrate, α-ketoglutarate, succinate, fumarate and malate. c Relative abundance of glutamine-derived 12C and 13C glutamine and glutamate. d Mass isotopologue distributions (MID) of TCA cycle intermediates, citrate, α-ketoglutarate, succinate, fumarate and malate. e Relative abundance of glutamine-derived 12C and 13C amino acids aspartate and proline. f Immunoblot for p70S6K and ribosomal S6 phosphorylation (pS6) in NV T-cells following 4 h activation with (anti-CD3/CD28) in the absence and presence of STAT5i (100 μM). β-actin was used as a loading control. Statistical analysis was performed using a paired t-test (f). Data are representative of four experiments (b–e) or three experiments (c) and are expressed as mean + SEM. **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001