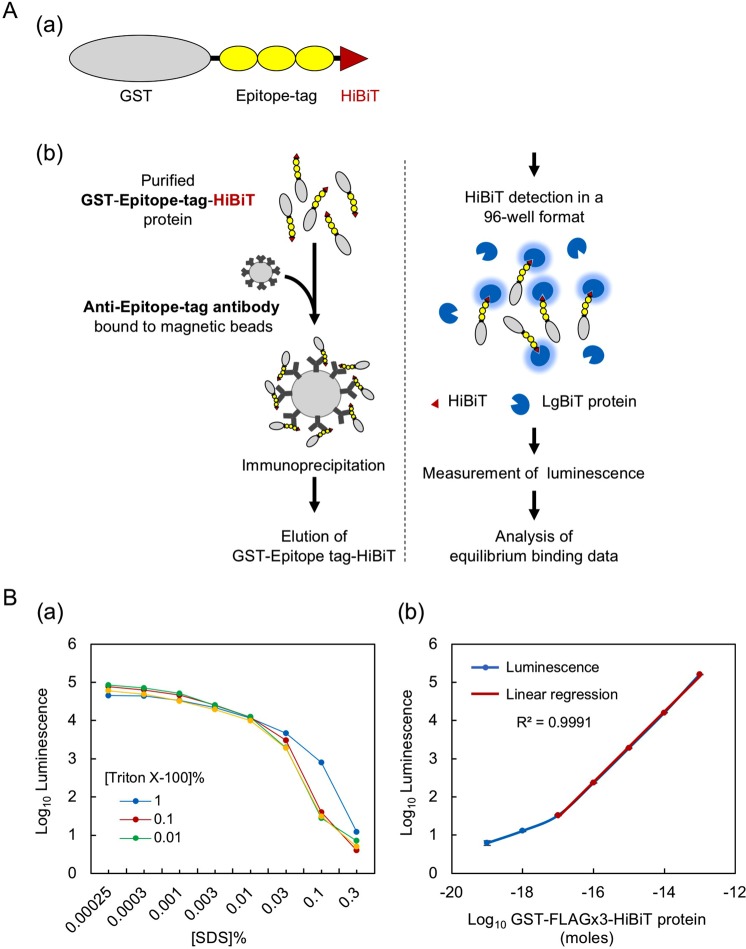
Figure 1.
HiBiT-based quantitative immunoprecipitation. (A) Design of the assay. (a) Schematic representation of the GST-epitope tag-HiBiT fusion protein. The coding region of the GST gene is C-terminally fused to the FLAG, HA, V5, PA or Ty1 epitope tags in their monomeric, dimeric or trimeric form and the HiBiT peptide, which is placed in the most C-terminal position. In this panel, the trimeric form of the epitope tags is shown as an example; the tags are not drawn to scale. (b) Illustration showing the main steps of the HiBiT-qIP assay and the principle of HiBiT detection. The details are provided in the main text. (B) HiBiT protein quantitation in the presence of SDS. (a) Effect of SDS and Triton X-100 on the HiBiT solution assay. To examine the effects of SDS on the enzymatic activity of reconstituted NanoLuc, 0.2 ng of GST-FLAGx3-HiBiT protein was included in 20 µL of PBS containing one of a series of concentrations of SDS (0.00025 to 0.3%), and the luminescence was measured after the addition of HiBiT detection reagents. The optimal Triton X-100 concentration for quenching the SDS effect was determined by adding Triton X-100 at three different concentrations, as indicated. (b) Linearity of the luminescence generated by HiBiT-LgBiT under our assay conditions. A tenfold dilution series of GST-FLAGx3-HiBiT protein (3.3 fg [10−19 moles] to 3.3 ng [10−13 moles]) in 20 µL of PBS containing 0.001% SDS, 0.01% BSA and 0.1% Triton X-100 was used in the HiBiT solution assay.