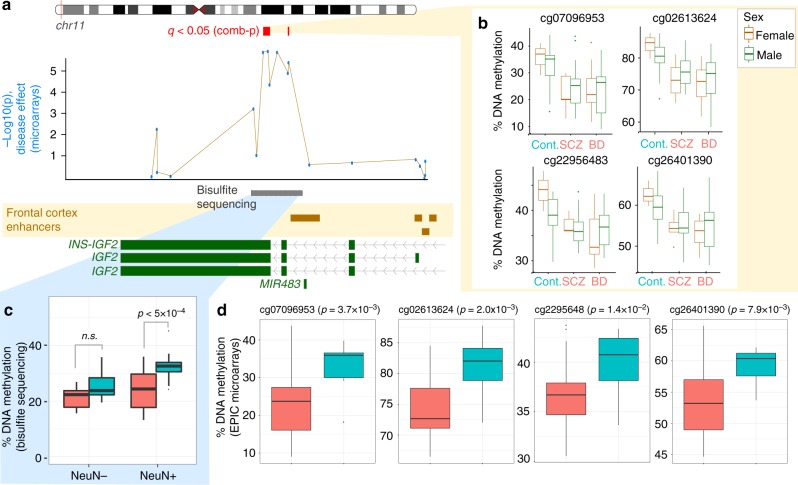
Fig. 2.
An enhancer at IGF2 is differentially methylated in neurons of major psychosis patients. a Hypomethylation in psychosis at the IGF2 locus. The view shows differentially methylated regions (red, comb-p) and nominal probe-level p-values (blue) in major psychosis cases (n = 55 individuals) relative to controls (n = 27 individuals), as identified by EPIC arrays. Also shown are adult frontal cortex enhancers (brown rectangles; NIH Roadmap Epigenomics Project) and region validated by targeted bisulfite sequencing (gray rectangle). b CpG probe-level methylation within differentially methylated IGF2 region, by diagnostic subgroup and sex. Boxplot center indicates median; box bounds indicate 25th and 75th percentile, and whiskers mark 1.5 times the interquartile range. c Validation of IGF2 hypomethylation using targeted bisulfite sequencing. Average % DNA methylation in a region in IGF2 that is differentially methylated in major psychosis. Box plots show the % DNA methylation averaged over the ~1.3 kb enhancer region in neuronal DNA (NeuN+; 13 cases, 13 controls) and glial DNA (NeuN-: 10 cases, 12 controls). Bases with ≥10× coverage are included in the analysis. P-value from ANOVA for effect of disease, after controlling for age, sex, post-mortem interval, and batch effect. Base-level methylation estimates from EPIC arrays and targeted bisulfite sequencing were strongly correlated (Pearson’s coefficient R = 0.67, p < 10−19; t-test; Supplementary Fig. 9). Boxplot elements same as in b. d Validation of neuronal IGF2 hypomethylation in cases, when samples are limited to males of European genetic ancestry (n = 25 cases, 11 controls). Nominal p-values from a nested ANOVA model for effect of diagnosis after controlling for age, post-mortem interval, and the first two genetic principal components. b–d Boxplot center indicates median; box bounds indicate 25th and 75th percentile, and whiskers mark 1.5 times the interquartile range. Boxplot elements same as in b