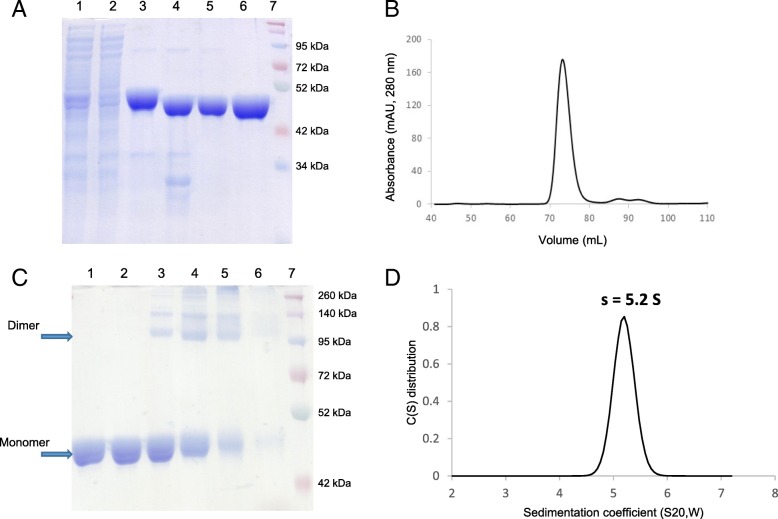
Fig. 2.
Purification of RelSt3 protein and determination of its oligomeric state. a Different steps of RelSt3 purification from E. coli (12% SDS-PAGE). Crude extract (lane 1) was submitted to a His-Trap affinity chromatography. Flow-through analysis (lane 2) indicated that most of the protein was retained. The pool of imidazole elution fractions (lane 3) was then digested by the TEV protease to remove His-tag (lane 4), and the sample was then loaded on a second His affinity chromatography. Without tag, the protein was not retained (lane 5), and was concentrated to be injected on a gel filtration column. Finally, the resulting RelSt3-containing fractions were concentrated (lane 6). Lane 7 corresponds to the Spectra Multicolor Broad Range protein ladder (Thermo Scientific). The gel was stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue. b Gel filtration (Sephadex 200) analysis of RelSt3 protein. The elution profile recorded showed a large main peak with a maximum elution volume of 72.4 ml. c Glutaraldehyde cross-linking of RelSt3 purified protein. 5 μg of RelSt3 protein were incubated without (lane 1) or with 0.001% (lane 2), 0.01% (lane 3), 0.025% (lane 4), 0.05% (lane 5) or 0.1% (lane 6) of glutaraldehyde. The products were then analyzed by SDS-PAGE (10%), with a Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining. See Materials and Methods for details. Lane 7: Spectra Multicolor Broad Range protein ladder. d Analysis of the dispersion state of RelSt3 by analytical ultracentrifugation. Sedimentation velocity of RelSt3 was analyzed at 5 μM. The diagram represents the sedimentation coefficient distribution [c(s)]