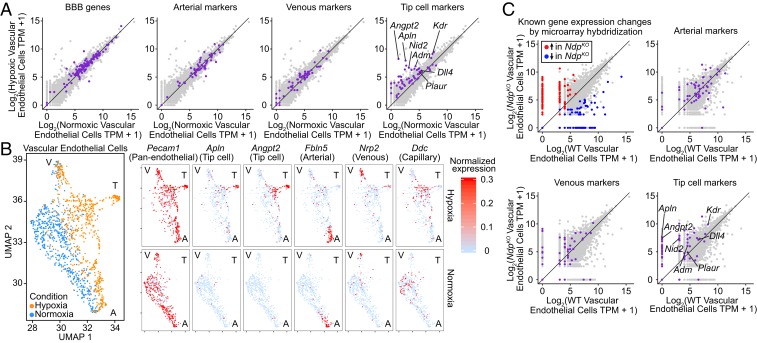
Fig. 7.
Brain and retinal vascular ECs activate the tip cell transcriptional program in response to chronic tissue hypoxia. (A) Scatterplots showing TPM for all transcripts expressed in normoxic and/or hypoxic cortical ECs (light gray) obtained by pooling transcript counts in the cortical scRNA-seq dataset. Transcripts previously defined as enriched in BBB-type, arterial, venous, or tip cell ECs are colored purple on individual plots. A 45° line is shown in each plot. (B, Left) UMAP plot for hypoxic and normoxic cortical ECs. (B, Right) Separate plots for each transcript showing hypoxic vs. normoxic cortical ECs [based on the combined UMAP plot (B, Left)] color coded by the level of normalized expression for a panendothelial marker (Pecam1), two tip cell markers (Apln and Angpt2), an arterial marker (Fbln5), a venous marker (Nrp2), and a capillary marker (Ddc). A, artery; T, tip cell; V, vein. (C) Scatterplots as in A showing TPM for all transcripts expressed in WT and NdpKO retinal ECs (light gray) obtained by pooling transcript counts in the retina scRNA-seq dataset. (C, Upper Left) Transcripts previously shown by microarray hybridization of immunoaffinity-purified ECs to be up- or down-regulated in NdpKO compared with WT ECs are highlighted (14). (C, Upper Right and Lower Right) Transcripts previously defined as enriched in arterial, venous, or tip cell ECs are colored purple on individual plots. A 45° line is shown in each plot.