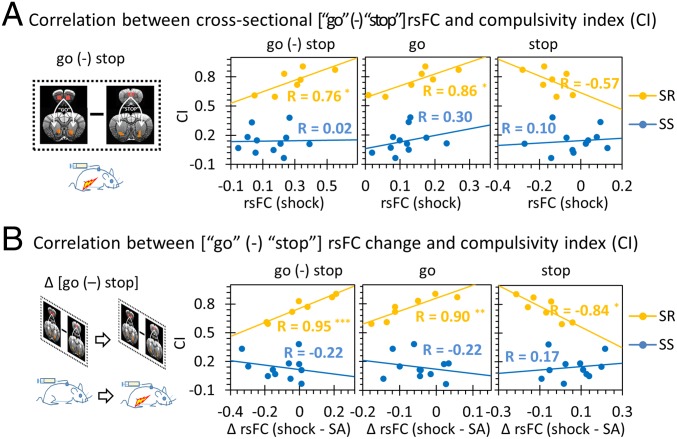
Fig. 5.
The relationship between the [go (-) stop] rsFC balance and the CI (Fig. 1B). (A) The cross-sectional [go (-) stop] balance significantly correlated with CI in SR rats (P = 0.047), with the go circuit significantly potentiating compulsive-like behavior (P = 0.014). (B) Longitudinal change in the [go (-) stop] balance after punishment positively correlated with the CI but only in the SR individuals (P = 0.0008), with a positive correlation with the go circuit change (P = 0.006) and negative correlation with the stop circuit change (P = 0.018). The CI was not correlated with rsFC change of the [go (-) stop] balance, nor any single circuit in the SS rats. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.