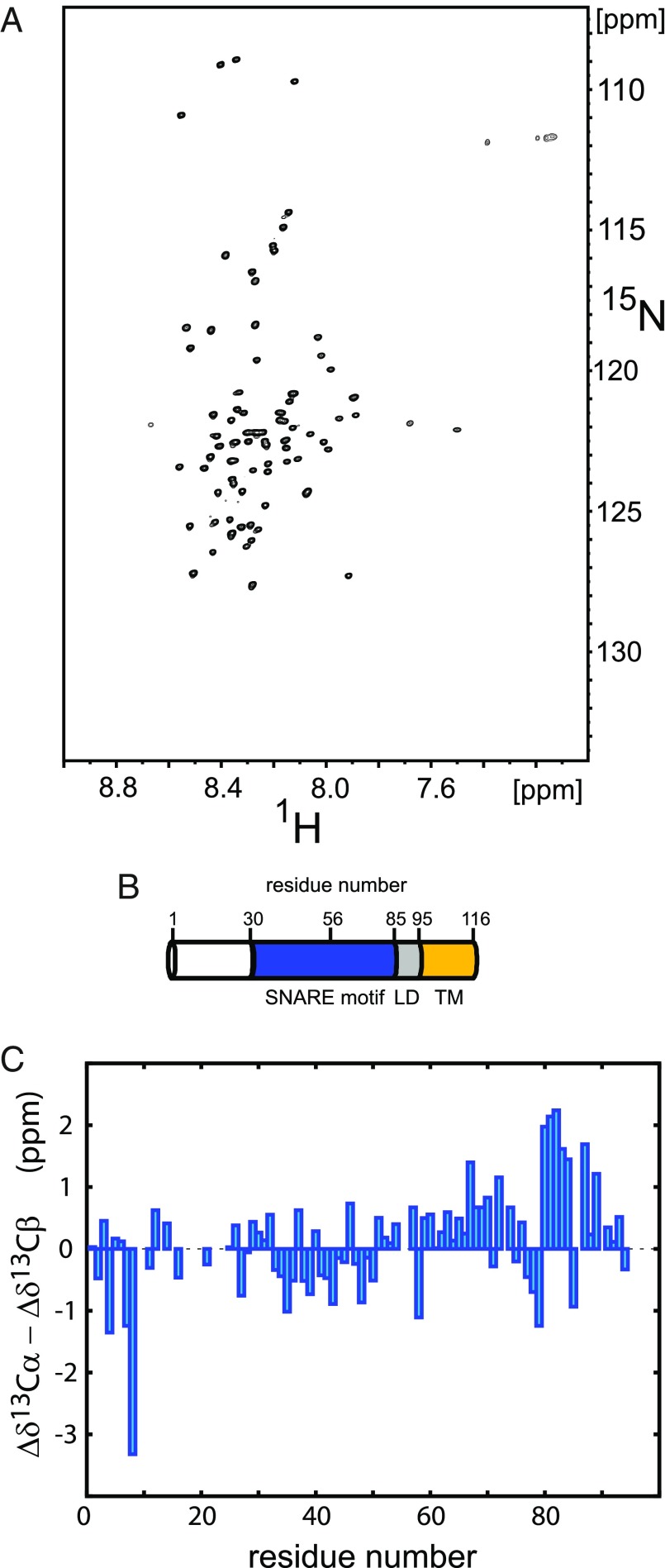
Fig. 1.
NMR analysis of syb-2. (A) Representative 2D 1H-15N TROSY-HSQC spectrum of 200 μM uniformly 2H,13C,15N-enriched syb-2 (1–96) dissolved in 20 mM MES buffer (pH 6.1), containing 250 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, and 0.1 μM TCEP, recorded at 800-MHz magnetic field strength and 5 °C. (B) Schematic view of the domain structure of syb-2 (1–116). Residue numbers above the cylinder indicate the boundaries of the SNARE motif, the zero layer, the LD, and the TMR, respectively. (C) Cα − Cβ secondary chemical shifts (Δδ13Cα − Δδ13Cβ), plotted as a function of amino acid sequence number [values around zero (between −1 and 1) indicate random coil-like behavior, and positive values (>1) indicate α-helical propensity (around 3–4 for fully α-helical)]. Data reveal increased α-helical propensity for the C terminus of the SNARE motif and the N terminus of the adjacent LD. The strongly negative outlier for Val-8 can be explained by nearest neighbor effects due to Pro-9 (48).