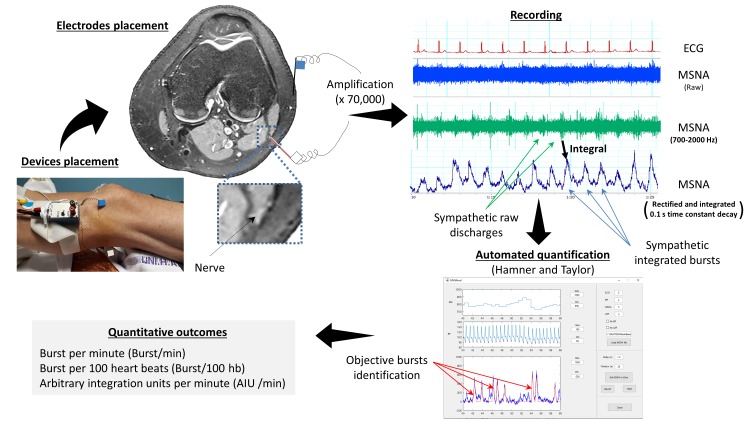
Figure 1.
Settings, acquisition, recording and reporting of muscle sympathetic nerve activity (MSNA). Measurement of MSNA is obtained by placement of an uninsulated tungsten register electrode in the peroneal nerve in the popliteal fossae or close to the fibula head. The objective is to reach postganglionic efferent sympathetic neurons. Potential voltage signal is recorded between the nerve electrode and a reference electrode placed on the external side of the knee. The acquired electrical signal is then amplified, band-filtered (700–2000 Hz), rectified and integrated. Sympathetic bursts, which correspond to nerve firing, are detected and scored using an automatic software in order to minimise subjective interpretation of the signal. MSNA results may be expressed in number of bursts per min or per 100 heartbeats, burst/min and bursts/100 heartbeats, respectively, or using the sum of areas under the curve of all burst in arbitrary integration units per minute or per 100 heartbeats, AUI/min and AUI/100 heartbeats, respectively.