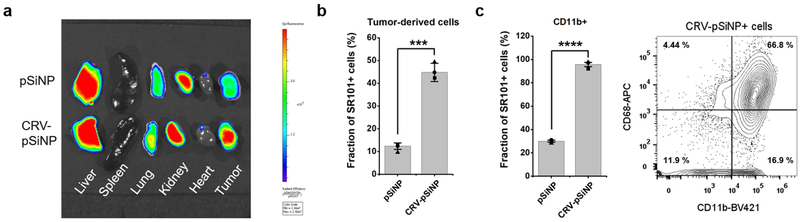
Fig. 7.
CRV facilitates delivery of nanomaterials to TAMs. (a) Biodistribution of CRV-pSiNPs in 4T1 tumor-bearing mice after IV injection. The experiments were performed in three animals per group and a representative fluorescence images of tumors and control tissues are shown. Top row: tissues from a mouse injected with SR101-loaded pSiNPs. Bottom row: tissues from a mouse injected with SR101-loaded CRV-pSiNPs. (b-c) Flow cytometry analysis of tumor cells isolated from 4T1 tumors after in vivo pSiNP or CRV-pSiNP homing. Cells were incubated with the indicated antibodies as described in Materials and Methods and the analysis was performed in three animals per group. (b) Percentages of SR101+ cells in whole tumor-derived cell population. Shown is mean ± SEM with individual data points overlaid as dots. Two tailed Student’s t-test was performed. t= 11.89. *** P = 0.0003. (c) Correlation between pSiNPs and macrophage markers. Left: Percentages of SR101+ cells in CD11b+ tumor-derived cells, t = 32.91, **** P = 0.000005. Right: phenotypic analysis of CRV-pSiNP-SR101+ tumor cells for CD11b and CD68. BV421: Brilliant Violet 421. APC: allophycocyanin.