Figure 8.
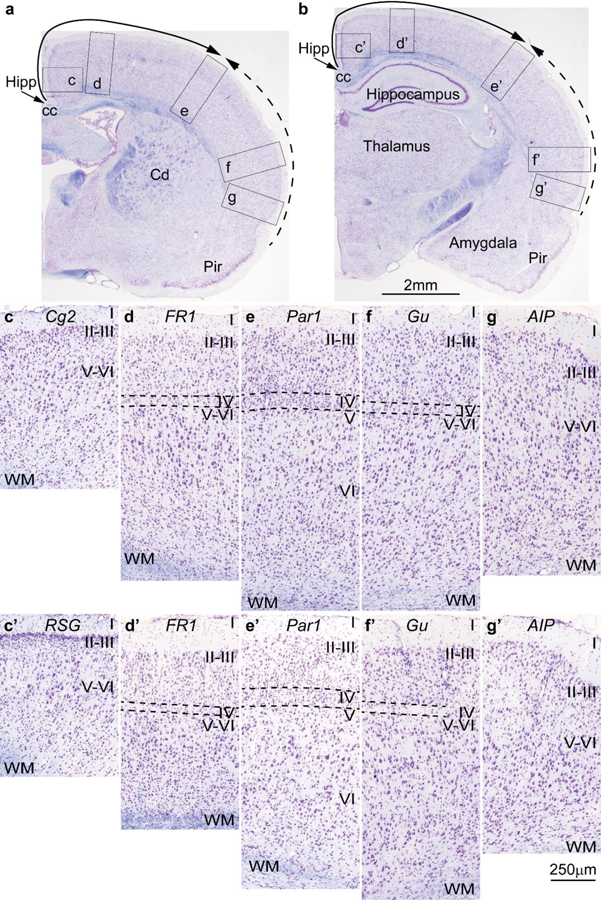
Cortical types and laminar gradients of differentiation in the cerebral cortex of the adult rat (stained for Nissl –purple- and myelin –blue-). Areas are named according to Zilles (1985). a, b, Photomicrographs of coronal sections in an adult rat brain stained for Nissl and myelin show the levels of photomicrographs c-g (from a) and c’-g’ (from b); the solid and dashed arrows show trends of increasing laminar differentiation. c-c’, Cingulate area 2 (Cg2) and the granular retrosplenial cortex (RSG) are found next to the anterior extension of the hippocampal formation (Hipp in a, b) and lack layer IV. d-d’, Frontal cortex, area 1 (FR1, primary motor cortex) has rudimentary layer IV (dashed lines). e-e’, Parietal cortex, area 1 (Par1, primary somesthetic cortex) has identifiable layer IV (dashed lines). f-f’, The gustatory cortex (Gu) has rudimentary layer IV (dashed lines). g-g’, The posterior part of the agranular insular cortex (AIP) is next to the piriform cortex (Pir in a, b) and lacks layer IV. Abbreviations: AIP: agranular insular cortex, posterior part; cc: corpus callosum; Cd: caudate; Cg2: Cingulate area 2; FR1: Frontal cortex, area 1 (primary motor cortex); Gu: gustatory cortex; Hipp: anterior extension of the hippocampal formation; Par1: Parietal cortex, area 1 (primary somesthetic cortex); Pir: piriform cortex in the primary olfactory cortex; RSG: granular retrosplenial cortex; WM: white matter. Roman numerals indicate cortical layers. Calibration bar in b applies to a-b. Calibration bar in g’ applies to c-g and c’-g’. [Note: This figure is an examination of material from a gift of Dr. Alan Peters].
