Fig. 8.
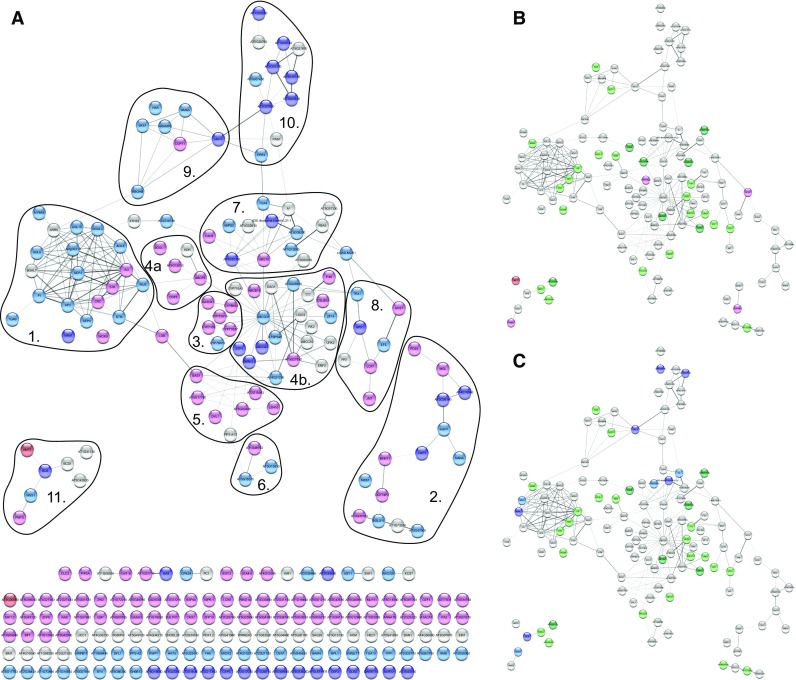
The results of in silico study of STRING software for protein–protein interaction network for 310 sex-specific DEGs. There were gene expression differences between the female and male lines (a). Proteins in red were detected only in female lines, while proteins in light red were more abundant in the female shoot apex than in the male shoot apex. Similarly, proteins in blue were present only in male lines, while proteins in light blue were more abundant in the male shoot apex than in the female shoot apex. Nodes in gray were not differentially expressed between the male and female lines. The thickness of edges corresponds to the confidence of the protein connection (thicker line = greater confidence in the connection). b Main network in the female vs hermaphrodite comparison; Proteins in red were detected only in female lines, while proteins in light red were more abundant in the female shoot apex than in the hermaphroditic shoot apex. Similarly, proteins in green were present only in hermaphrodite lines, while proteins in light green were more abundant in the hermaphrodite shoot apex than in the female shoot apex. Nodes in gray were not differentially expressed between the hermaphrodite and female lines. c Main network in the male vs hermaphrodite comparison. Proteins in blue were detected only in male lines, while proteins in light blue were more abundant in the male shoot apex than in the hermaphroditic shoot apex. Similarly, proteins in green were present only in hermaphrodite lines, while proteins in light green were more abundant in the hermaphrodite shoot apex than in the male shoot apex. Nodes in gray were not differentially expressed between the hermaphrodite and male lines. Networks were prepared using the STRING program and then visualized with Cytoscape
