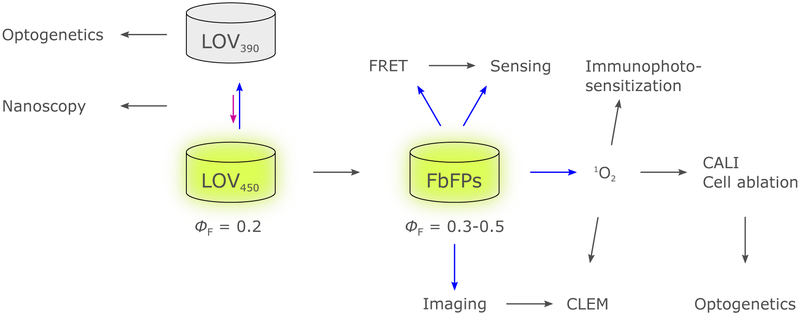
Figure 25.
Overview of the properties and biophysical applications of flavin-binding fluorescent proteins (FbFPs). Constitutively fluorescent FbFPs are engineered from wild-type LOV domains, by substituting the active-site cysteine to abrogate canonical LOV photochemistry, and by introducing other mutations to increase the fluorescence quantum yield ΦF. They can be used for imaging in fluorescence microscopy, as donors in FRET and as fluorescence-based sensors.350–353 The photochromicity of cysteine-retaining LOV domains can be exploited in cellular super-resolution microscopy (nanoscopy),157–159 while formation of the thioadduct in LOV domains underlies conventional optogenetic applications. In addition, FbFPs can function as genetically-encoded photosensitizers for 1O2, with a range of further applications.354,355 Blue and purple arrows indicate excitation with blue or violet light, respectively.