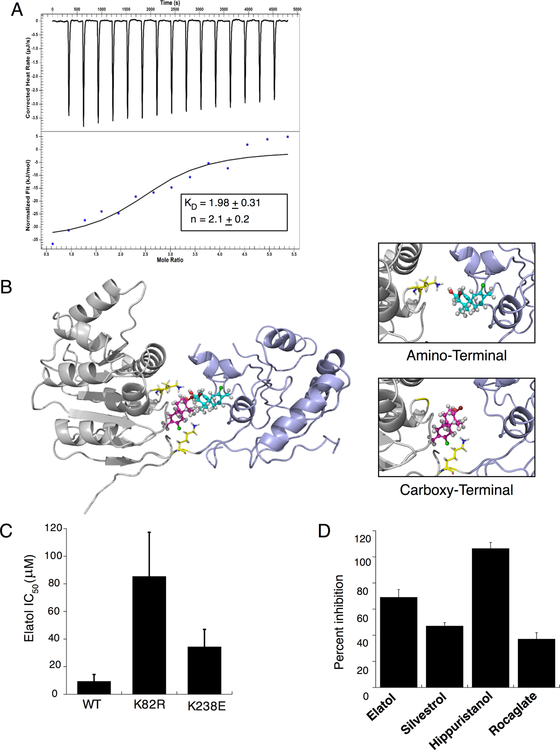
Figure 2.
Elatol binds to the N- and C-termini of eIF4A in a 2:1 stoichiometry. A) Isothermal titration calorimetry of eIF4A1 and elatol. Data fit to an independent binding model using NanoAnalyze software from TA instruments. Mean ± SEM n=3 B) Putative elatol binding with eIF4A1 based on molecular modeling experiments shows two elatol molecules (blue and pink) interacting with key lysines (yellow) in the RNA binding groove between the two helicase domains of eIF4A (gray and purple). C) Malachite green assay for ATP hydrolysis showing IC50 for elatol treatment against wildtype eIF4A1 or proposed lysine mutants in the proposed binding sites. Mean ± SEM n=3 D) eIF4A helicase activity measured following treatment with various known eIF4A inhibitors and elatol. Mean ± SEM n=3.