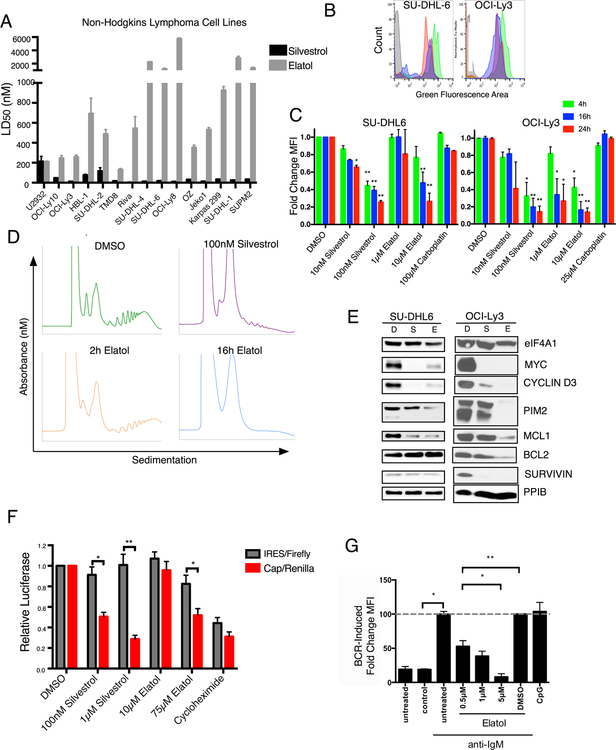
Figure 3.
Elatol is toxic to Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma cell lines and inhibits protein translation A) Sensitivity of a collection of Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma cell lines to known eIF4A inhibitor silvestrol or elatol. Viability measured after 72-hour treatment using Promega Cell Titer Glo reagent. LD50 calculated using nonlinear regression fit analysis in Graphpad Prism 7. Mean ± SEM n=4. B) Histogram plot showing OPP labeling in DLBCL cell lines treated with DMSO (green), 100 nM silvestrol (red) or 10 μM elatol (blue) for 24 hours. Unlabeled cells shown in gray. C) Mean fluorescent intensity of live cells labeled with OPP in DLBCL cells treated with indicated concentrations of silvestrol, elatol, or carboplatin for four, 16 or 24 hours. Normalized to DMSO control. Mean ± SEM n=3. * = p< 0.05, ** = p<0.001. D) Polysome profiling of OCI-Ly3 cells treated with DMSO or 100nM silvestrol for 2 hours or 2 μM elatol for 2 or 16 hours. E) Western blot showing protein expression of translationally regulated genes in DLBCL cells treated with DMSO (D), 50 nM silvestrol (S) or 5 μM elatol for 16h. Representative images, n=3. F) Dual luciferase reporter assay measuring cap-dependent versus IRES mediated luciferase expression following an eight-hour treatment with the indicated translational inhibitors. Relative luciferase units normalized to DMSO-treated cells. Mean −/+ SEM, n=3 G) Translation measured by OPP incorporation in CD19+CD5+ CLL patient cells following anti-Ig-M stimulation and elatol treatment. Normalized to anti-Ig-M stimulated but untreated cells. CpG-ODN stimulation used as a control. Mean ± SEM n=4. * = p< 0.05, ** = p<0.001.