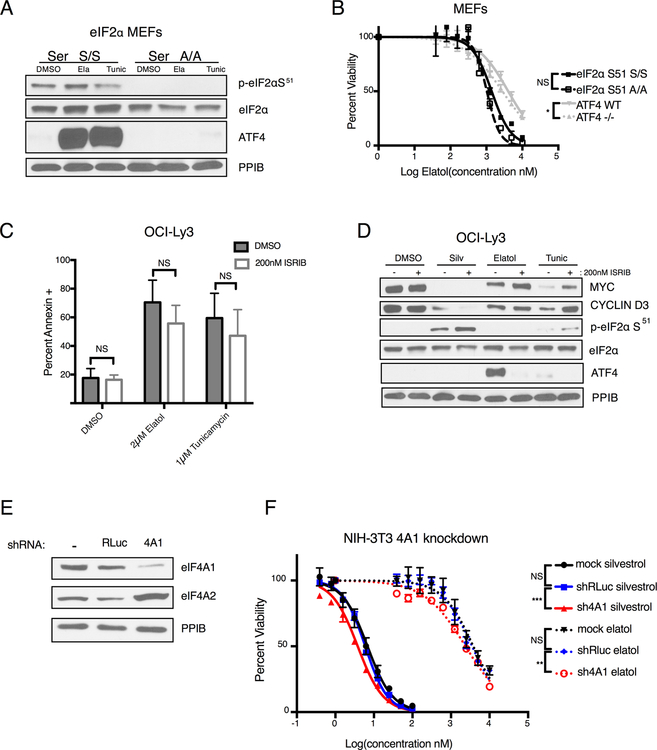
Figure 5.
Elatol induction of ATF4 is mediated by eIF2α phosphorylation, but toxicity is dependent on eIF4A inhibition. A) Western blot showing protein expression in eIF2α wildtype and Ser51 A/A mutant MEFs treated with DMSO, 5 μM elatol or 5 μM tunicamycin for 8 hours. B) Cell viability in MEF cells wildtype or homozygous mutant for alanine at serine 51 of eIF2α and wildtype or homozygous knockout of ATF4 measured using Cell Titer Glo following 72 hour treatment with elatol. Mean ± SEM n=4 * = p< 0.05, ** = p<0.001. C) Western blot showing protein expression in cells treated for four hours with DMSO, 100 nM silvestrol, 5 μM elatol or 5 μM tunicamycin with or without the combination with 200 nM ISRIB. Representative images. n=3. D) Cell death measured by flow cytometry following annexin V staining in DLBCL cell lines treated with indicated inhibitors with or without the combination of the 200 nM ISRIB. Mean ± SEM n=3. * = p< 0.05, ** = p<0.001. E) Western blot showing eIF4A1 and eIF4A2 protein levels in NIH-3T3 cells stably expressing shRLuciferase (shRLuc) control or eIF4A1 shRNA transfected with the indicated proteins. Representative images, n=2. F) Viability of NIH-3T3 cells stably expressing control or eIF4A1 shRNA measured by Cell Titer Glo after being treated with the indicated compounds for 5 days. Mean ± SEM n=4. * = p< 0.05, ** = p<0.001, ***=p<0.0001