Figure 6.
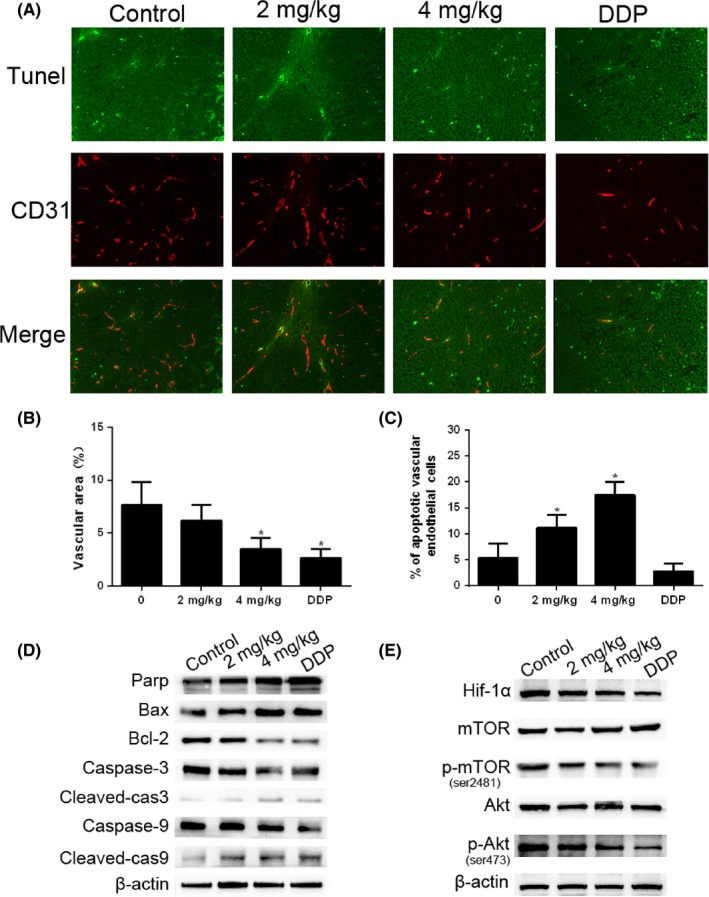
Cinobufagin induces apoptosis of endothelial cells in vivo. A, Apoptotic vascular endothelial cells were detected using TUNEL and CD31 staining in tumor tissues from BALB/c nude mice with treatment (0, 2 mg/kg, 4 mg/kg of cinobufagin and 0.5 mg/kg of cisplatin) (n = 6). Double‐stained cells indicate apoptotic endothelial vascular cells (green) in the tumor tissues (200×). Anti‐CD31 antibody was used as a marker for endothelial cells (red). B, Area of tumor endothelial cells (red) was quantified by Image‐Pro Plus 6.0 (IPP6) software. C, Percentage of apoptotic endothelial cells (double stained) in tumor issues. Immunostained plugs were assessed by microscopy at 200× magnification. *P < .01 compared with control group. D, Effect of cinobufagin on the caspase pathway (Bax, Bcl‐2, caspase‐3, cleaved‐caspase‐3, caspase‐9 and cleaved‐caspase‐9) in tumor tissues. Western blot analysis was carried out to detect changes in the levels of different groups of mice. E, Effect of cinobufagin on the expression of hypoxia‐inducible factor 1α (HIF‐1α), mTOR, p‐mTOR (ser2481), Akt, and p‐Akt (ser473). DDP, cis‐diamminedichloroplatinum
