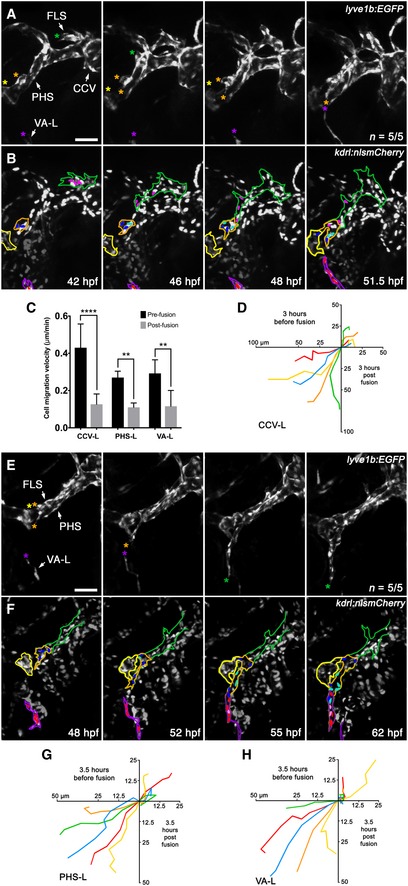
-
A, B
Still images from
Movie EV3 of early facial lymphatic development in a
lyve1b:EGFP (A),
kdrl:nlsmCherry (B) compound transgenic from 42 to 51.5 hpf, with the CCV‐L‐derived leading tip cell (green asterisk), the PHS‐LP domains (orange and yellow asterisk) and the distal tip of the VA‐L (purple asterisk) highlighted (A). Between 42 and 46 hpf, the PHS‐LP
P (orange outline) cells divide (dark blue parent cells, light blue daughter cells) before sprouting as lymphangioblasts from the PHS and fusing with the tip (pink cells) of the CCV‐derived FLS (green outline) at 48 hpf (B). Cells (red) within the VA‐L (purple outline) can also be seen migrating towards the now PHS‐L‐derived FLS tip by 48 hpf. The PHS‐LP
A is also shown (yellow outline).
-
C
Quantitation of leading lymphangioblast velocity (μm/min) before and after fusion with another lymphangioblast [CCV‐L‐derived FLS tip (pink cells) to PHS‐L (B, blue cells; n = 5/5) and PHS‐L‐derived FLS tip (blue cells) to VA‐L (F, red cells; n = 5/5)] or by the VA‐L to the PHS‐L‐derived FLS tip (B, n = 5/5).
-
D
Cell migration tracks where each coloured track depicts the distance (μm) travelled over 3 h by the leading tip cell in a separate animal before and after fusion with the CCV‐L‐derived FLS tip (pink cells) and the PHS‐Ls (B, blue cells; n = 5/5).
-
E, F
Still images from
Movie EV4 of facial lymphatic development in a
lyve1b:EGFP (C),
kdrl:nlsmCherry (D) compound transgenic from 48 to 62 hpf showing that after the CCV‐derived FLS fuses to the PHS‐L, these take over as the leading tip cells (orange asterisks), with one PHS‐L migrating anteriorly to fuse with PHS‐LP
A (yellow asterisk), and others migrating ventrally to fuse with the VA‐L (purple asterisk) (C). After the PHS‐derived portion (orange outline) of the FLS (green outline) fuses to the VA‐L (purple outline), migration of the entire facial lymphatic pauses to allow for lymphangioblast proliferation (dark blue and red parent cells, light blue and pink daughter cells) before resuming migration anteriorly along the ventral base of the eye (D).
-
G, H
Cell migration tracks where each coloured track depicts the distance (μm) travelled over 3.5 h by the leading tip cell in a separate animal before and after fusion with another lymphangioblast [PHS‐L‐derived FLS tip (blue cells) to VA‐L (F, red cells; n = 5/5)] or by the VA‐L to the PHS‐L‐derived FLS tip (F, n = 5/5).
Data information: Error bars represent standard deviation; ****
P <
0.0001, **
P <
0.01 by unpaired Student's
t‐test. CCV, common cardinal vein; CCV‐L, common cardinal vein‐derived lymphangioblast; FLS, facial lymphatic sprout; hpf, hours post‐fertilisation; PHS, primary head sinus; PHS‐L, primary head sinus‐derived lymphangioblast; PHS‐LP
A, anterior primary head sinus lymphatic progenitor domain; PHS‐LP
P, posterior primary head sinus lymphatic progenitor domain; VA‐L, ventral aorta lymphangioblast. Scale bar = 50 μm.