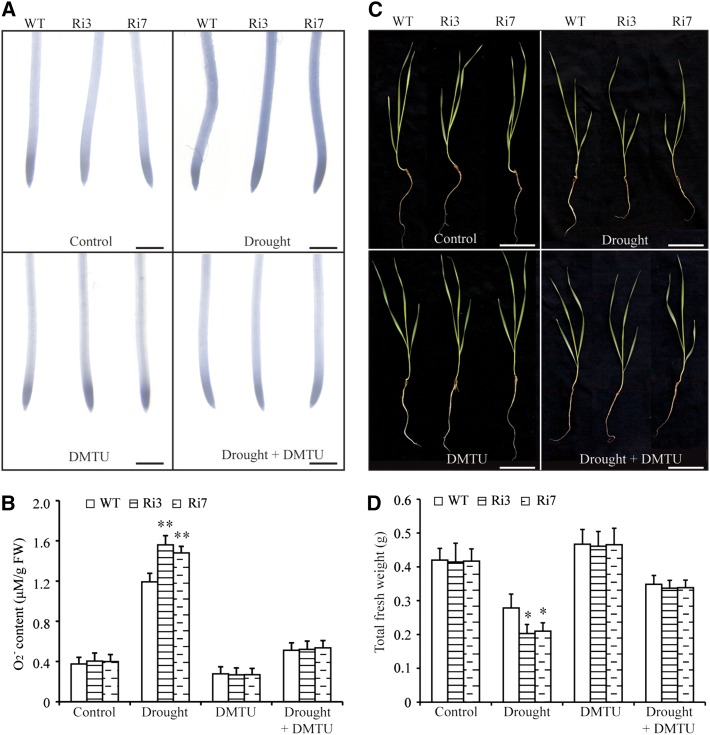
Figure 5.
TaBZR2 functions positively in scavenging drought-induced O2−. A, NBT staining in primary root tips of TaBZR2-RNAi and wild-type wheat plants grown in half-strength Hoagland’s liquid medium, medium containing 15% (w/v) PEG 6000, medium containing 1 mm of DMTU, or medium containing 15% (w/v) PEG 6000 + 1 mm of DMTU for 72 h. The strength of color shows the concentration of O2− in the root tips. Scale bar = 1 mm. B, Measurements of the O2− contents of TaBZR2-RNAi and wild-type wheat plants grown in half-strength Hoagland’s liquid medium, medium containing 15% (w/v) PEG 6000, medium containing 1 mm of DMTU, or medium containing 15% (w/v) PEG 6000 + 1 mm of DMTU for 72 h. Each data point is the mean (±se) of six biological replicates. The asterisks indicate significant differences between TaBZR2-RNAi and wild-type wheat plants (Student’s t test, **P < 0.01). C, Phenotypes of TaBZR2-RNAi and wild-type wheat plants grown in half-strength Hoagland’s liquid medium, medium containing 15% PEG 6000, medium containing 1 mm of DMTU, or medium containing 15% (w/v) PEG 6000 + 1 mm of DMTU. Scale bar = 2 cm. D, Measurement of the total fresh weight of TaBZR2-RNAi and wild-type wheat plants grown in half-strength Hoagland’s liquid medium, medium containing 15% (w/v) PEG 6000, medium containing 1 mm of DMTU, or medium containing 15% (w/v) PEG 6000 + 1 mm of DMTU. Each data point is the mean (±se) of six biological replicates. The asterisks indicate significant differences between TaBZR2-RNAi and wild-type wheat plants (Student’s t test, *P < 0.05). WT, wild type.