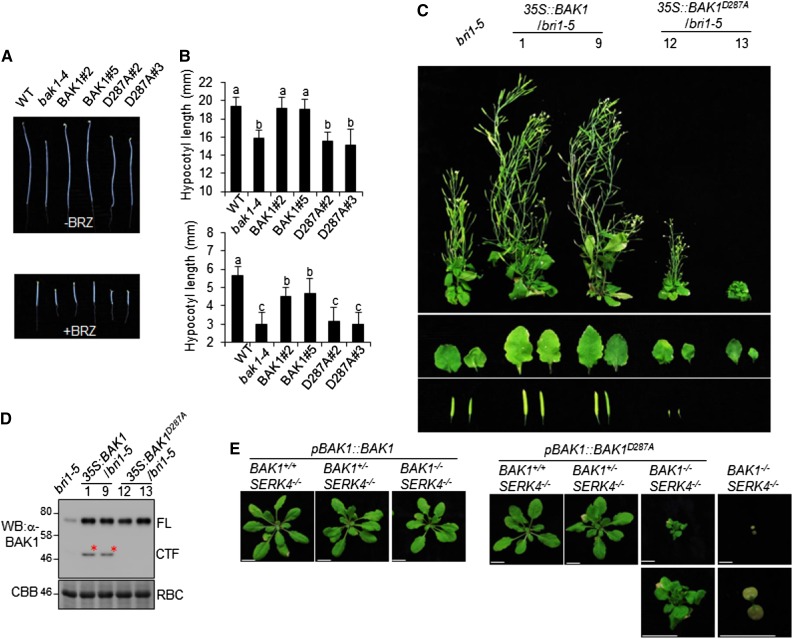
Figure 5.
BAK1 D287 is critical for BR signaling and cell death control. A, The reduced hypocotyl length of pBAK1::BAK1D287A/bak1 transgenic plants. The seedlings of wild-type, bak1-4, and transgenic plants were grown in the dark for 5 d on 1/2 MS plates without or with 1 μm of brassinazole. B, Quantification of the hypocotyl length shown in (A). The data are shown as the mean ± sd from 20 biological repeats. The different letters indicate statistically significant difference analyzed with one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s test (P < 0.05). C, BAK1D287A mutant cannot restore bri1-5 dwarf defect. Transgenic plants of 35S::BAK1 and 35S::BAK1D287A in bri1-5 background were photographed at 2 months old. The individual leaves and siliques are shown in the middle and bottom. D, Expression of BAK1 protein in rosette leaves from 4-week-old plants of (C) was detected by western blot (WB) with an α-BAK1 antibody. E, D287 is important for BAK1 function in cell death control. Arabidopsis BAK1+/−SERK4−/− plants were transformed with pBAK1::BAK1 or pBAK1::BAK1D287A. Plants of T1 generation after selection of BAK1 or BAK1D287A transgene were genotyped for endogenous genomic BAK1. Pictures were taken 4 weeks after germination. The above experiments were repeated three times with similar results. BAK1+/+SERK4−/− (BAK1: wild type; SERK4: mutant); BAK1+/−SERK4−/− (BAK1: heterozygous, SERK4: mutant); BAK1−/−SERK4−/− (BAK1: mutant, SERK4: mutant); WT, wild type. Scale bars = 1 cm.