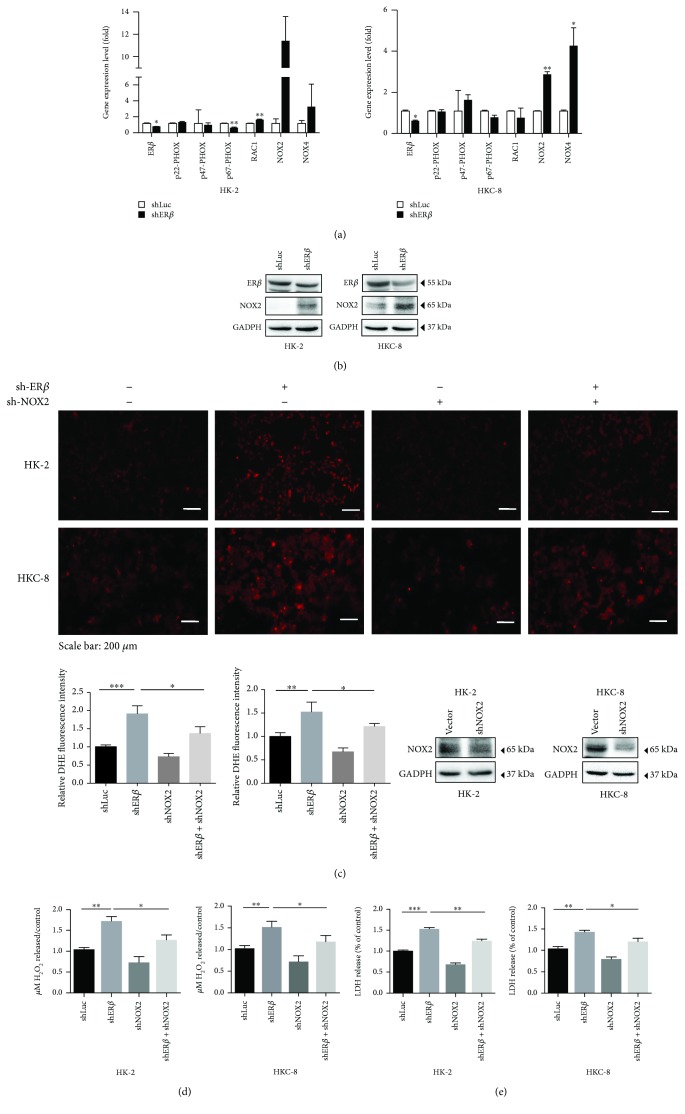
Figure 3.
ERβ inhibits oxalate-induced oxidative stress via modulating NOX2 expression. (a) The qRT-PCR analysis of NADPH oxidase subunits after knocking down ERβ in HK-2 and HKC-8 cells. Cells were transduced with shERβ or with shLuc as control after 72 hr incubation, and then treated with 0.75 mM oxalate for 6 hr. (b) Western blot analysis of NOX2 expression in renal cells with/without shERβ after 6 hr exposure to 0.75 mM oxalate. (c) Rescue assay using HK-2 and HKC-8 cells with/without shERβ. shNOX2 showed partially reversed knockdown of ERβ- (shERβ-) induced ROS production. All cells were exposed to 0.75 mM oxalate for 6 hr prior to collection for data analysis. Upper panels show representative images of DHE staining, and quantification is shown in the lower left panel. Western blot in the lower right panel shows NOX2 knockdown efficiency. (d) After treating with 0.75 mM oxalate for 6 hr, shNOX2 can partly reverse the silenced ERβ-induced H2O2 production in conditioned media. (e) Rescue assay using HK-2 and HKC-8 cells with/wthout shNOX2 showed partially reversed shERβ-induced LDH release. All the cells in Figures 3(a)–3(e) were exposed to 0.75 mM oxalate for 6 hr prior to collection for data analysis. For (a), (c), (d), and (e), data are presented as mean ± SD. ∗ P < 0.05, ∗∗ P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗ P < 0.001.