Fig. 3.
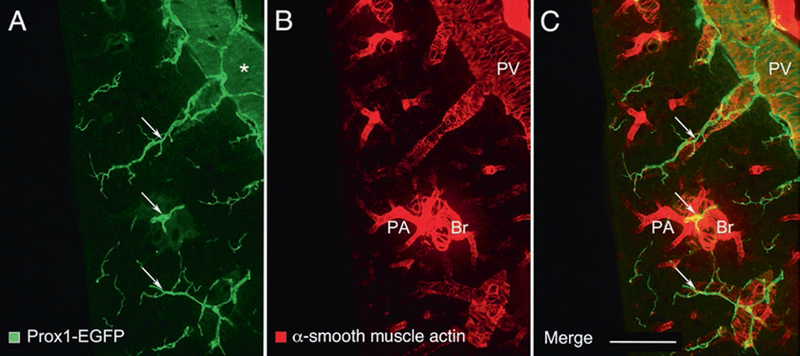
Enlargements of a region near the center of Fig. 2. Left lung of a normal adult C57BL/6 Prox1-EGFP mouse stained for (a) Prox1-EGFP (green) and (b) alpha-smooth muscle actin (red). (c) merged image. Lymphatics (arrows) generally follow the scaffold of smooth muscle cells of airways and blood vessels, especially pulmonary veins (PV): Peripheral branches of the bronchus (Br) and pulmonary artery (PA) are closely associated in pairs, and separate from branches of the pulmonary vein. Each type of vessel has a characteristic coat of smooth muscle cells. The proximal portion of the pulmonary vein has a coat of cardiac muscle cells (asterisk), which express Prox1-EGFP, but are more weakly stained than lymphatics, and also has a thin coat of smooth muscle cells. Scale bar: 500 μm
