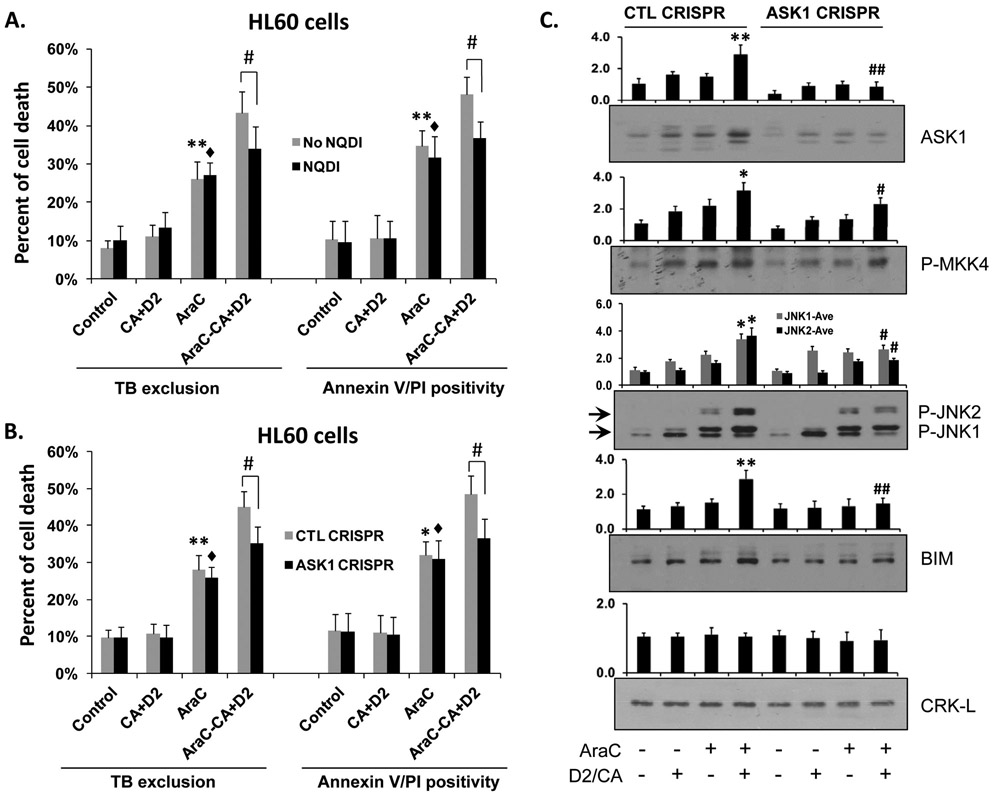
Figure 5.
A. Inhibition of ASK1 by specific pharmacological inhibitor NQDI-1 or B. Knock down of ASK1 by CRISPR/Cas9 in HL60 cells reduces AraC/D2/CA induced cell death in ECD. *, p<0.05, **, p<0.01 vs the Control group; ♦; p<0.01 vs the NQDI or ASK1 CRISPR Control group; #, p<0.01 when comparing CTL CRISPR-ECD with VDR CRISPR-ECD, as indicated in the bar charts. C. Western blots were performed for ASK1, and its direct downstream targets, phosphorylated MKK4 and JNK, and the apoptosis regulator BIM. Note the enhanced ECD-associated increase in these markers, and their decrease by ASK1 knock down. CRK-L was used as a loading control. The average of relative signal intensities from three separate experiments are shown in bar charts above each blot. *, p<0.05; **, p < 0.01 vs the AraC group; #, p<0.01 when comparing CTL CRISPR-ECD with VDR CRISPR-ECD.