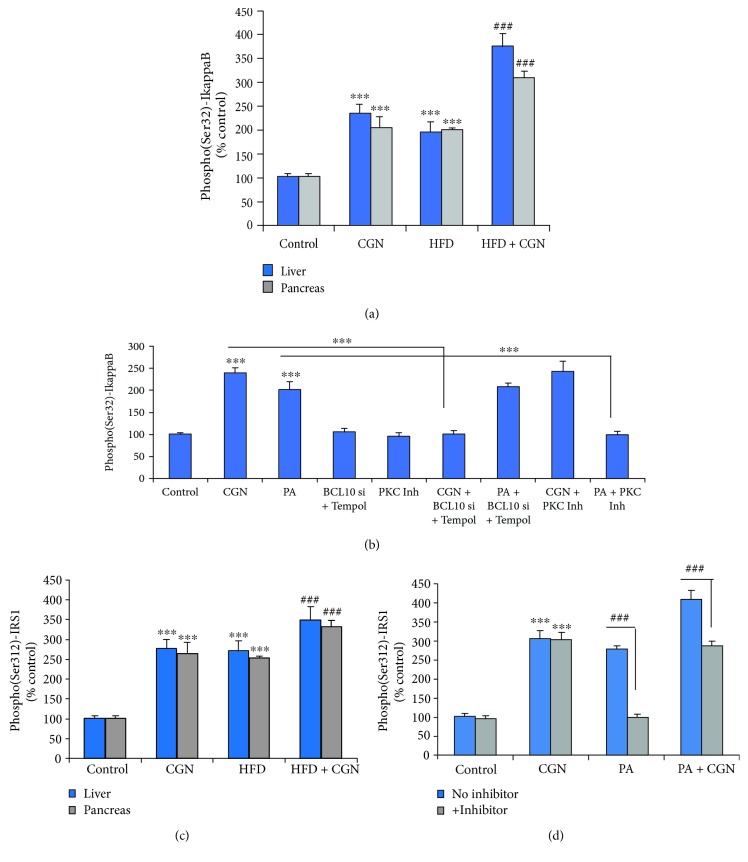
Figure 2.
Distinct mechanisms lead to increases in phospho(Ser32)-IκBα and phospho(Ser307/312)-IRS1. (a) Phospho-IκBα was increased in the hepatic and pancreatic tissues of the mice (p < 0.001, n = 12). The combination yielded a significantly greater increase (p < 0.001). (b) Palmitic acid also increased the phospho(Ser)-IκBα. The effect of palmitic acid was inhibited by sotrastaurin but not by the combination of Tempol and BC10 siRNA, which inhibited the carrageenan-induced effects (p < 0.001, n = 3). (c) Phospho(Ser307/312)-IRS1 increased in the hepatic and pancreatic tissues of the treated animals (p < 0.001, n = 12). The increase by the combination of carrageenan and HFD was significantly greater. (d) The palmitic acid-induced increase in phospho(Ser307/312)-IRS1 was blocked by exposure to the PKC inhibitor sotrastaurin (p < 0.001, n = 3). CGN = carrageenan; IRS = insulin receptor substrate; PA = palmitic acid; PKC = protein kinase C.