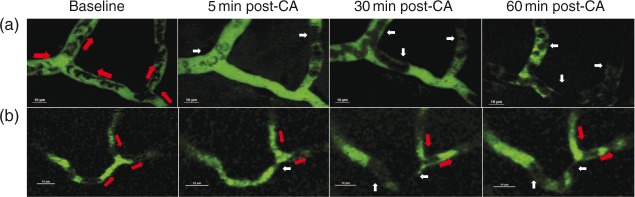
Figure 3.
Capillary RBC flow after CA. Upper panel: Illustration of RBC stasis (no-reflow phenomenon) in representative capillaries in vivo. Panels A and B represent two individual capillaries with stagnant RBCs post-CA from two rats. Both capillaries were continuously perfused with red blood cells (RBCs) prior to CA. Red arrows indicate the flow direction in every capillary branch. White arrows indicate stagnant RBCs. In panel A, RBC flow was stagnant in all branches at 5, 30 and 60 min post-CA. In panel B, RBC flow in the left branch was stagnant at 5, 30 and 60 min post-CA, while the RBC flow in the other two branches was continuous.