Figure 1.
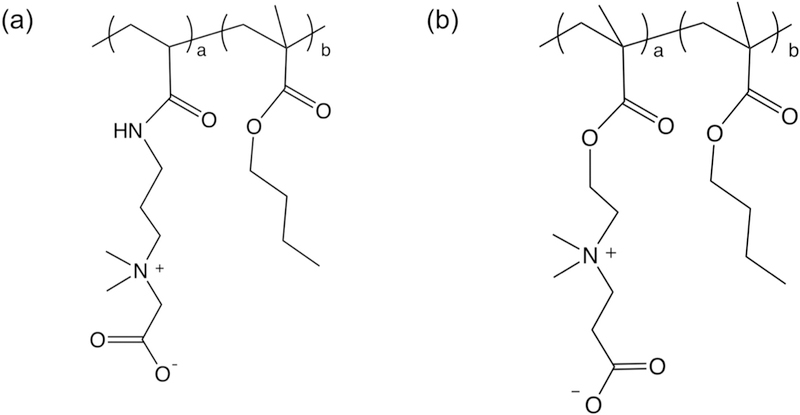
Chemical structures of synthetic carboxybetaine (CB) random copolymers. (a) poly(CB1-co-BMA) (PCB1), and (b) poly(CB2-co-BMA) (PCB2). 1 and 2 behind CB stand for number of carbon spacer between carboxyl groups and quaternary ammonium cations. The composition of each unit in the copolymer was calculated through integration of characteristic protons in 1H-NMR spectrum, where 3.82 ppm (-CH2-,2H) for the CB1 unit, 2.42 ppm (-CH2-,2H) for the CB2 unit, and 1.45–1.63 ppm (-CH2-,4H) for the BMA unit. The carboxyl groups in PCB2 can be activated by EDC/NHS chemistry, and covalently bond with amino groups of, for example, proteins, enzyme, and aptamer/oligonucleotides.
