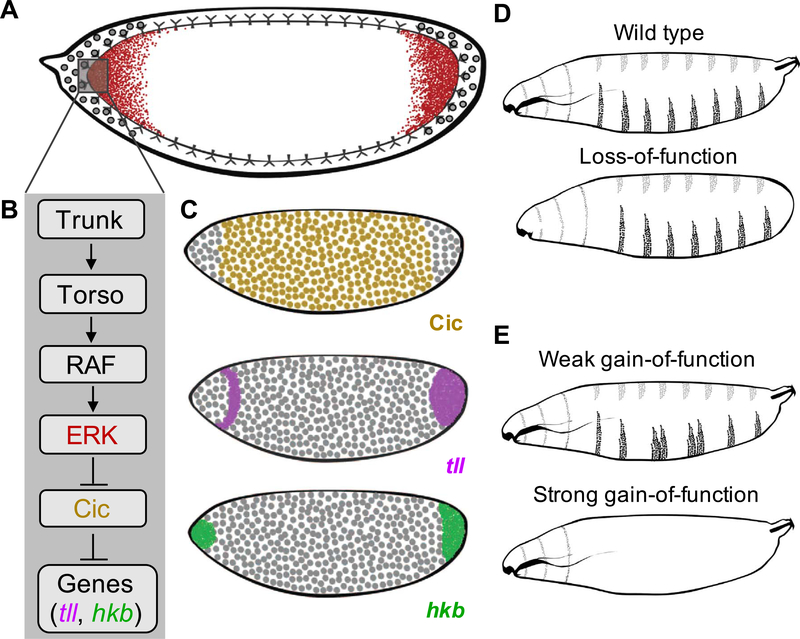
Fig. 1.
Torso-mediated ERK activation in the early Drosophila embryo. (A) A cartoon of the RTK Torso driven ERK activation (red) in the early fly embryo. (B) Schematic of the Torso pathway. (C) Active ERK induces expression of terminal genes such as tailless (magenta) and huckebein (green) by antagonizing Capicua-mediated repression (yellow). (D, E) Schematics representing the larval cuticle phenotype for wild type (D), loss-of-function (LOF) (D), and gain-of-function (GOF) backgrounds (E) in the Torso pathway.