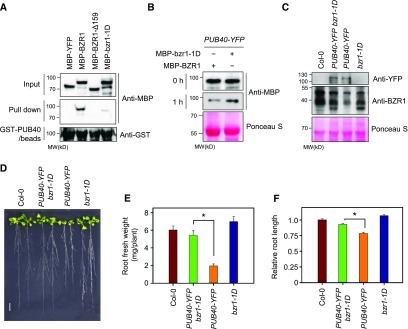
Figure 6.
The bzr1-1D Mutation Reduces PUB40-Mediated BZR1 Degradation.
(A) The binding affinity of PUB40 for bzr1-1D protein. Equal amounts of MBP-YFP, MBP-BZR1, MBP-BZR1-∆159 (∆149 to Δ307), or MBP-bzr1-1D (P234L) were pulled down with GST-PUB40–bound beads. Immunoblots were probed with anti-MBP and anti-GST antibodies.
(B) bzr1-1D degradation by PUB40. Equal amounts of MBP-YFP and MBP-bzr1-1D were incubated with protein extracts from 35S-PUB40-YFP plants. Ponceau S staining was used as a loading control.
(C) Endogenous BZR1 levels in the roots of PUB40-YFP bzr1-1D. PUB40-YFP and BZR1 were detected with anti-YFP and anti-BZR1 antibodies, respectively. Ponceau S staining was used as a loading control.
(D) Phenotypes of Col-0, PUB40-YFP, bzr1-1D, and bzr1-1D overexpressing PUB40-YFP. Plants were grown on MS medium for 14 d. Scale bar = 1 cm.
(E) Measurement of root fresh weight per seedling shown in (D). Error bars = ±se. Asterisks (*) indicate significant differences by Student’s t test (P < 0.001). Three roots were grouped and weighed at one time (n = 10). The data shown are representative of three independent experiments.
(F) Measurement of root length in the seedlings shown in (D). Error bars = ±se (n > 30 per genotype). Asterisks (*) indicate significant differences by Student’s t test (P < 0.001). The data shown are representative of two independent experiments.