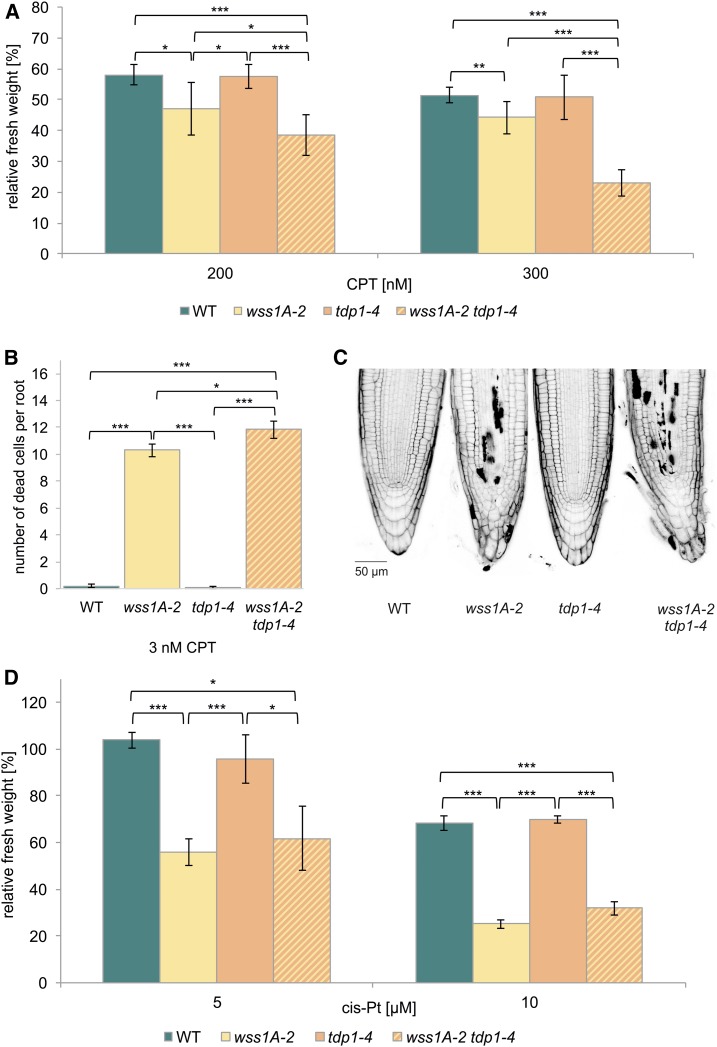
Figure 6.
Analysis of a wss1A-2 tdp1-4 Double Mutant.
(A) Mean values of plantlet fresh weights of the wss1A-2 tdp1-4 double mutant, the corresponding single mutant lines and the wild type (WT), relative to untreated controls after treatment with 200 and 300 nM CPT (n = 6). The wss1A-2 tdp1-4 double mutant exhibited synergistic sensitivity effects with both CPT concentrations used, compared with both single mutants. Although the wss1A-2 allele was hypersensitive, tdp1-4 revealed relative fresh weights comparable with wild type.
(B) and (C) Mean values of ten PI-stained root tips per line of the wss1A-2 tdp1-4 double mutant, the corresponding single mutant lines, and the wild type after induction with 3 nM CPT (n = 3) confirmed the synergistic sensitivity effect. Whereas in both wild-type and tdp1-4 lines less than one dead cell per root was detectable, 10 and 12 dead cells per root were shown for wss1A-2 and the double mutant, respectively, a significantly elevated cell death level compared with both single mutants.
(D) Mean values of plantlet fresh weights of the wss1A-2 tdp1-4 double mutant, the corresponding single mutant lines, and the wild type, relative to untreated controls after treatment with 5 and 10 µM cis-platin (cis-Pt; n = 3). The wss1A-2 tdp1-4 double mutant exhibited a hypersensitivity on wss1A single mutant level with both concentrations applied. Tdp1-4 did not show a hypersensitive effect and revealed a relative fresh weight comparable with wild type.
Columns in (A), (B), and (D) correspond to mean values, and error bars represent ±sd. Statistical differences were calculated using a two-tailed t test with unequal variances: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.