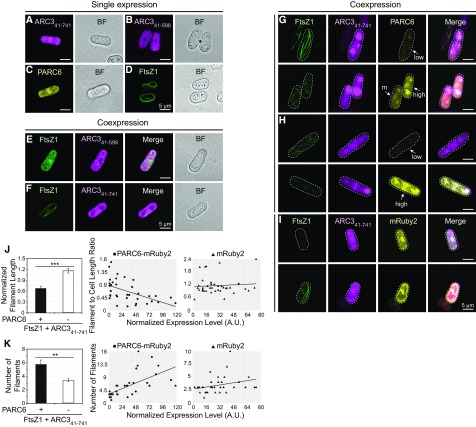
Figure 6.
Activation of Full-Length ARC3 by PARC6 Inhibits Assembly of FtsZ1 Filaments in S. pombe.
Epifluorescence and bright-field micrographs of transformed S. pombe cells expressing the indicated proteins are shown. In epifluorescence images, mVenus, mCerulean (mCer), and mRuby2 signals are falsely colored green, magenta, and yellow, respectively. Bars = 5 μm. BF, bright-field micrograph.
(A) to (D) Single-expression strains: (A) ARC341-741-mCerulean, (B) ARC341-598-mCerulean, (C) PARC677-573-mRuby2, and (D) FtsZ1-mVenus.
(E) and (F) Effect of (E) ARC341-598-mCerulean and (F) ARC341-741-mCerulean on assembly of FtsZ1-mVenus filaments in coexpression strains.
(G) to (I) Effect of ARC341-741-mCerulean on assembly of FtsZ1-mVenus filaments in strains also coexpressing (G) and (H) PARC677-573-mRuby2 or (I) mRuby2. White arrows in (G) and (H) designate cells expressing PARC677-573-mRuby2 at high, moderate, or low levels as indicated by the mRuby2 signal intensity. Outlines of the imaged yeast cells are indicated by dashed lines. Additional details are described in the text. M, moderate.
(J) and (K) Quantitative analysis of the effect of ARC341-741-mCerulean on the assembly of FtsZ1-mVenus filaments in the presence of PARC677-573-mRuby2 (n = 36 cells) or mRuby2 (n = 37 cells). The effect on assembly was evaluated in individual cells based on (J) the length of FtsZ1-mVenus filaments and (K) the number of FtsZ1-mVenus filaments. In (J), filament length was normalized to cell length because cell length constrains filament length (TerBush and Osteryoung, 2012). Left panels show means and error bars are sem. ***P < 0.0001; **P < 0.001 as determined by the t test. In the middle and right panels, the x axis indicates the level of PARC677-573-mRuby2 or mRuby2 expression as indicated by the total fluorescence intensity normalized to the cell area. Slopes of the best-fit lines are as follows: (J) PARC677-573-mRuby2, −0.006 (R2 = 0.275); mRuby2, 0.002 (R2 = 0.006); (K) PARC677-573-mRuby2, 0.081 (R2 = 0.406); mRuby2, 0.026 (R2 = 0.089). A.U., arbitrary units.