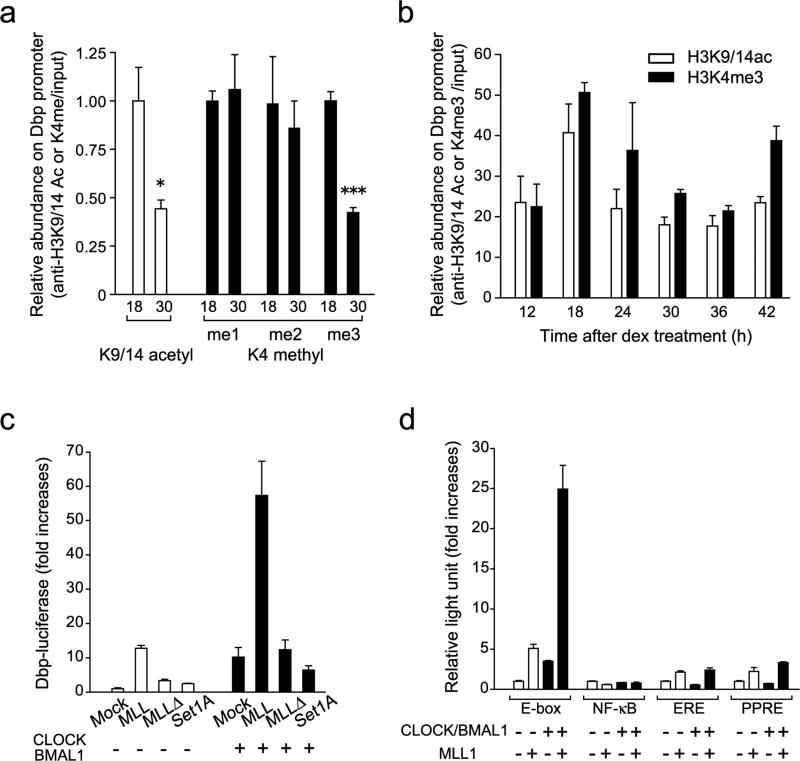
Figure 1. Histone H3K4 methyltransferase MLL1 synergistically activate CLOCK:BMAL1-mediated gene transcription.
(a) Me3 but not me1/2 level of H3K4 changes between two time points on the Dbp promoter E-box region. ChIP analyses were performed in MEFs at 18 or 30 hr after dexamethasone synchronization using antibodies against acetylated H3K9 and K14 (white) and me1, me2 or me3 H3K4 (black). (Means ±SEM of three independent samples, *p<0.05, and ***p<0.0001). The amount of highest modification time point (18 hr) was set to 1. (b) H3K4me3 follows same circadian rhythmicity as acetylation of H3K9/K14 on the Dbp promoter E-box region. ChIP analyses were performed in MEFs after dexamethasone synchronization. (Means ±SEM of three independent samples from a representative experiment. Analogous results were observed in three independent experiments). (c) Histone H3K4 specific-methyltransferase MLL1 and SET1A were transiently transfected with or without CLOCK:BMAL1 in 293 cells. MLL1 but not SET1A showed substantial increases of the dbp-luc transcription. On the other hand, methyltransferase-dead mutant of MLL1 (MLL1Δ)) abolished transcriptional activity. (Means ±SEM of eight samples in two independent experiments) (d) Synergistic transcriptional activation on E-box motif by MLL1 together with CLOCK:BMAL1. E-box motif-containing sequences (E-box), NF-κB-responsive element (NF-κB), estrogen responsive element (ERE) or PPARresponsive element (PPRE) luciferase reporter genes were transfected in presence or in absence of CLOCK:BMAL1 in 293 cells. (Means ±SEM of eight samples from two independent experiments).