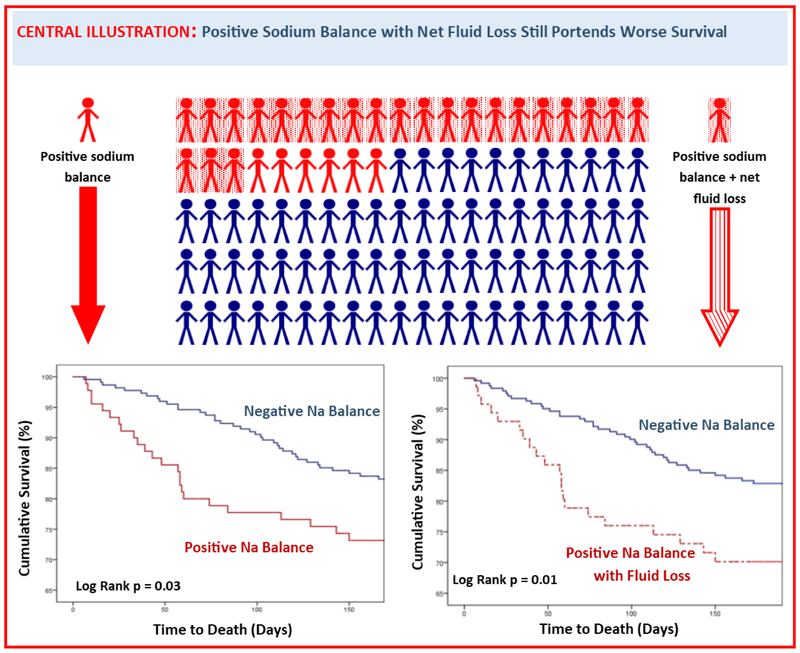
Central Illustration: Positive Sodium Balance with Net Fluid Loss Still Portends Worse Survival.
Urine sodium excretion, as metric of diuretic response, carries prognostic value. A considerable percentage (29%) of participants excreted less sodium than would be consumed in their diet (positive sodium balance), and these patients experienced decreased six-month survival (log rank p = 0.03). Even those who exhibited positive sodium balance and net fluid loss (23%) still experienced decreased survival (log rank p = 0.01).