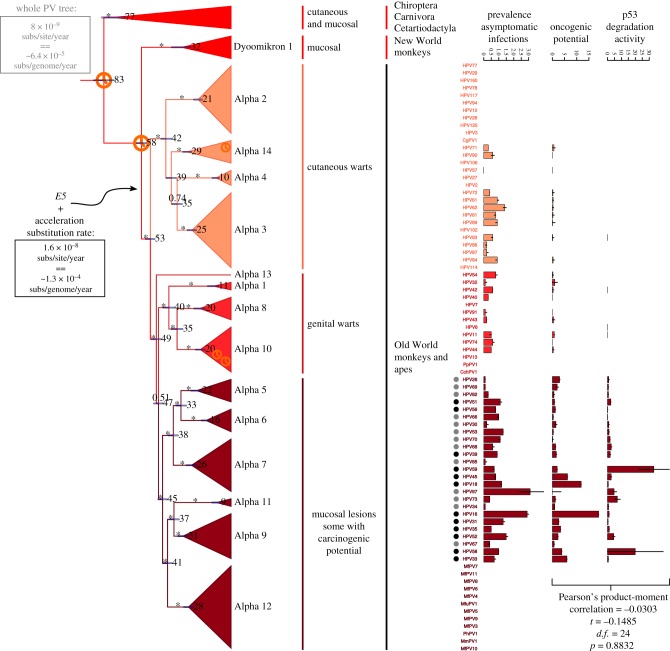
Figure 2.
This tree is a zoom in on the Alpha–Omikron PV crown-group shown in figure 1. Values at the nodes correspond to posterior probabilities, where asterisks indicate full support. Error bars encompass 95% highest posterior density for the age of the nodes; next to the error bars, the median node age is given in millions of years ago (Ma). Clock symbols indicate the nodes used for calibration. A black arrow indicates the timing for the emergence of E5 gene in the ancestral PV genome, between 53 and 58 Ma. Boxes display the average evolutionary rate for the complete PV tree (in grey) or for the AlphaPV subtree after the emergence of E5 (in black). On the right side of the tree, the different PV species, the clinical presentation and host taxonomy are given. Dots label HPVs that have been classified by the IARC as carcinogenic to humans (black dots, group I) or probably/possibly carcinogenic to humans (grey dots, groups IIa and IIb). The three barplots on the right represent: (a) the worldwide prevalence of each HPV in women with normal cervical cytology, with error bars indicating the 95% confidence interval; (b) the oncogenic potential for each HPV, proxyed as the ratio between the prevalence of each HPV in cervical cancers divided by the prevalence in normal cervical cytology), with error bars indicating the 95% confidence interval; (c) the E6-mediated p53 degradation activity, expressed as the inverse value of the EC50 in ng of E6 protein needed to degrade cellular p53, with higher values indicating an enhanced potential of E6 to degrade p53; error bars indicate an approximate of the standard error of the mean. The first two barplots contain data obtained from the ICO/IARC HPV Information Centre (http://www.hpvcentre.net/), while the third contains data obtained from Mesplede et al. [7]. The correlation analysis for the second and third barplot is shown in the inset at the bottom. For the raw data of the barplots, see electronic supplementary material, table S4. (Online version in colour.)