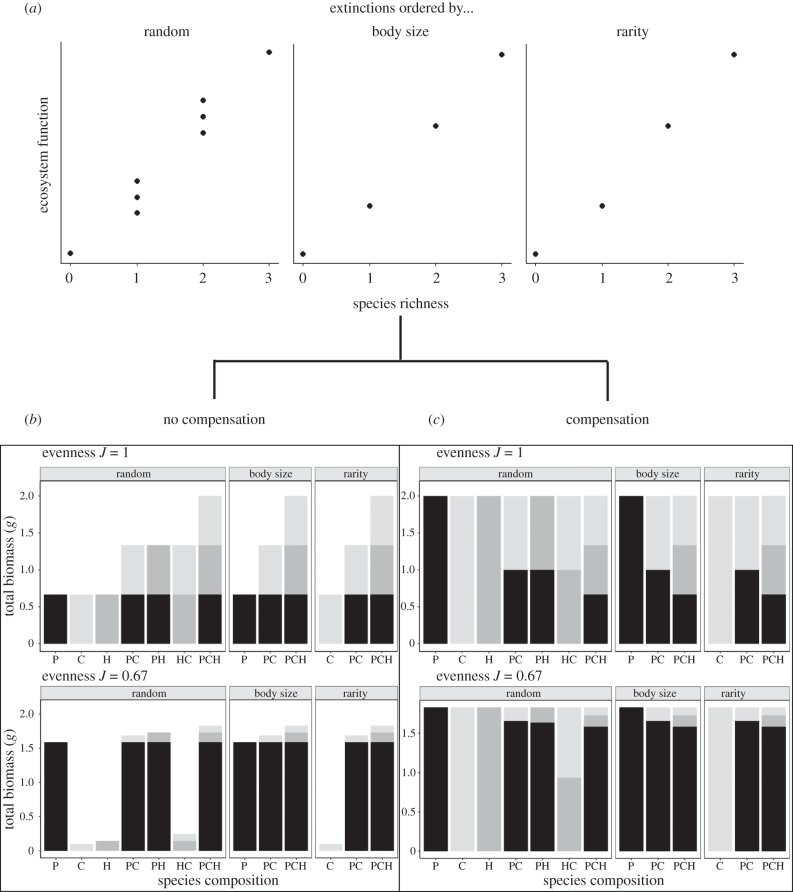
Figure 1.
Summary of the experimental design. Communities were assembled to reflect extinction scenarios that assumed (a) random extinction, representing the full spectrum of possible species combinations, versus trait-based extinctions ordered by body size (i.e. body mass) or relative abundance (rarity). Each scenario of extinction consisted of (b) a set of non-interactive communities that experienced no biomass compensation versus (c) a set of interactive communities that experienced complete biomass compensation in response to declining species richness. The design was repeated across two levels of evenness that represent those typical of experimental (J1) versus natural (J0.67) systems. C, Corophium volutator; H, Hediste diversicolor; P, Peringia ulvae for monoculture and combination of abbreviations for species mixtures. Shading of bars indicates the proportional representation of each species (C, light grey; H, dark grey; P, black).