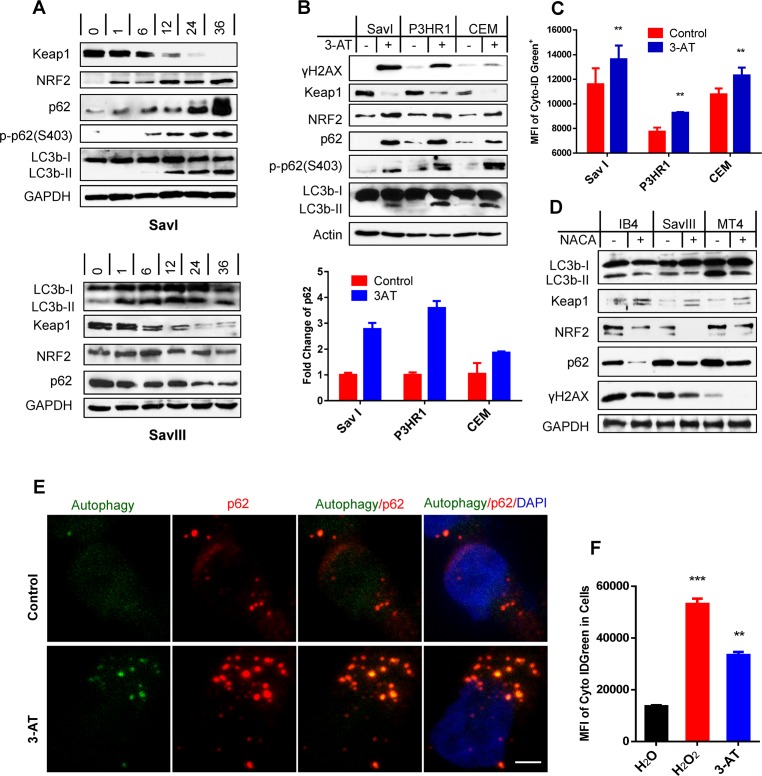
Fig 2. ROS correlate with Keap1-NRF2 pathway activity and contribute to p62 expression and activation of p62-mediated autophagy in viral latency.
A. SavI and SavIII cells, which were derived from the same patient, were treated with 2 µM of the topoisomerase II inhibitor doxorubicin HCl (Doxo) (UBPBio) for different time periods. B-C. SavI, P3HR1, and CEM were treated with 20 mM of the H2O2 catalase 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole (3-AT) (Fisher Scientific) or vehicle control for 48 h. Cells were then subjected to IB, qPCR, and flow cytometry analyses. D. IB4, LCL45, and MT4 were treated with 3 mM of the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine amide (NACA) (Sigma) or vehicle control for 30 h. The treated cells were then subjected to analyses for p62, autophagy, Keap1-NRF2 pathway, and ROS production. E. IB4 cells were treated with 20 mM 3-AT (Fisher Scientific) or vehicle control for 48 h, and analyzed for p62-autophagosome colocalization by confocal microscopy. Living cells were first stained with a Cyto-ID Autophagy Detection kit (Enzo), and then fixed for staining with the mouse p62 antibody (D-3) and Alexa 555 coupled anti-mouse antibody (Invitrogen). Bar = 2 µm. F. IB4 cells were treated with 50 µM H2O2 for 30 min and then medium was replaced and continued in culture for 2 days, or treated with 20 mM 3-AT for 48 h, before subjected to analysis of autophagy flux by flow cytometry with the Cyto-ID Autophagy Detection kit. MFI = mean fluorescence intensity.