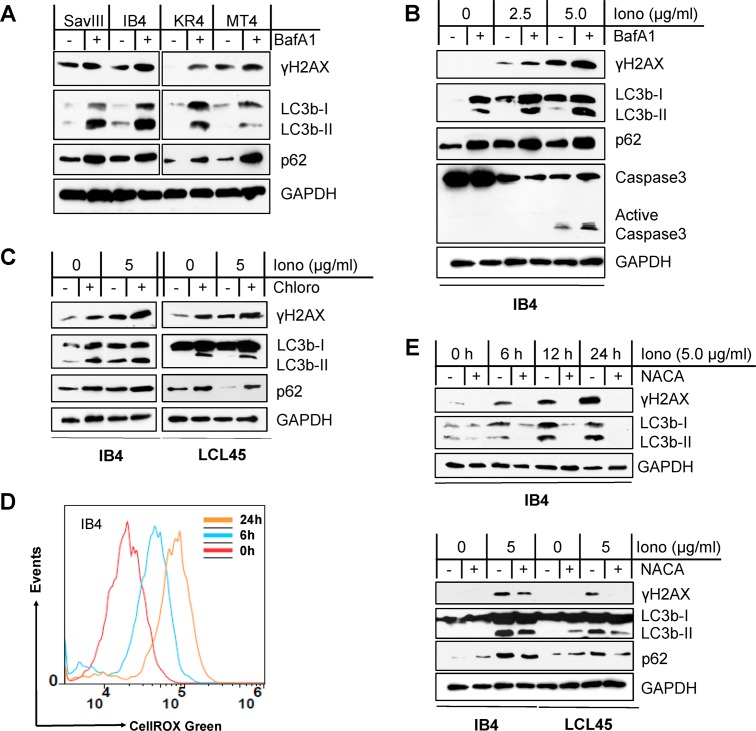
Fig 3. Autophagy inhibition sensitizes EBV+ cells to ROS-induced DNA damage that is associated with p62 accumulation.
A. Cell lines with higher endogenous autophagy levels were treated with 0.4 µM of the vacuolar ATPase inhibitor bafilomycin A1 (BafA1) (Sigma) or vehicle control for 24 h, and then DNA damage (γH2AX) was evaluated by immunoblotting. B-C. The LCL lines IB4 and LCL45 were treated with ionomycin (Iono) (Sigma) with indicated concentrations for 48 h plus 0.4 µM BafA1 or vehicle control for 24 h or plus 50 µM of the lysosome inhibitor chloroquine (Chloro) (MP Biomedicals) or vehicle control for 6 h. p62, autophagy, and γH2AX were analyzed by immunoblotting. D. IB4 cells were treated with 5 µg/ml Iono or vehicle control for different time periods, and ROS production was measured by flow cytometry with the CellRox Green reagent (Invitrogen). A representative result from three independent repeats is shown. E. IB4 and LCL45 cells were treated with 5 µg/ml Iono plus 3 mM NACA or vehicle control for different time periods (upper panel) or for 30 h (lower panel). p62, autophagy, and γH2AX were analyzed by immunoblotting.