Fig. 2|. Procedure for chemically defined differentiation of hiPSCs into hiPSC-CMs and downstream replating.
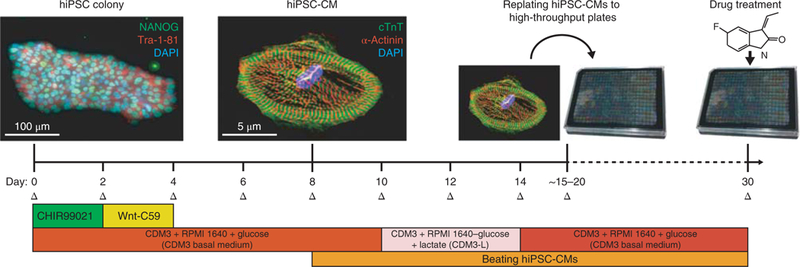
Initially, hiPSCs will exhibit a tightly packed colony morphology and will express stem cell markers such as NANOG (green) and Tra-1–81 (red). Nuclear DNA stain DAPI is also shown (blue). This differentiation approach requires small molecule-mediated modulation of the Wnt signaling pathway by GSK3β inhibitor CHIR99021 and Wnt inhibitor Wnt-C59 to drive hiPSCs toward a cardiac mesoderm and cardiomyocyte fate. Beating hiPSC-CMs are typically visible by day 8 of differentiation. After cardiomyocyte differentiation and metabolic selection are complete, hiPSC-CMs will be pure and will express cardiomyocytespecific markers such as cardiac troponin T (cTnT; green) and alpha-actinin (red). Nuclear DNA stain DAPI is also shown (blue). At this point, they can be replated into high-throughput plates for downstream drug treatment and analysis. Medium changes (Δ) should be conducted on hiPSC-CMs every 2 d. NANOG antibody (Abcam, cat. no. AB21624) and Tra-1–81 antibody (EMD Millipore, cat. no. MAB4381) were utilized at 1:200 dilutions (~5 μg/mL) for hiPSC immunofluorescence staining. Cardiac troponin T antibody (Abcam, cat. no. AB45932) and alpha-actinin antibody (Sigma, cat. no. A7811) were utilized at 1:200 dilutions (~5 μ/mL) for hiPSC-CM immunofluorescence staining. For further details on how immunofluorescence and hiPSC-CM differentiation were conducted, refer to our previous study, Sharma et al.10. The CDM3 added to RPMI1640 in this figure refers to the CDM3 supplement.
