Fig. 4.
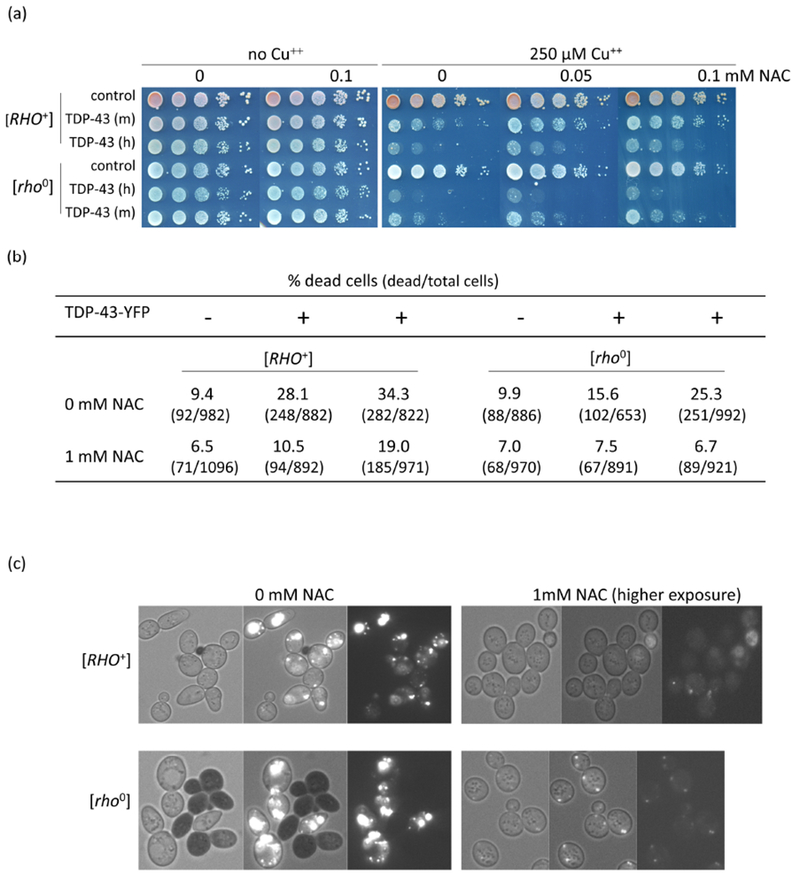
Antioxidant reduces TDP-43 level and toxicity. (a) Antioxidant reduces TDP-43 growth inhibition. Isogenic [RHO+] and [rho−] versions of CUP1-TDP-43-YFP (TDP-43) integrants with medium (m) and high (h) levels of toxicity and vector (control) grown on plasmid selective medium were normalized, serially diluted (1/10) and spotted on plates with the indicated levels of CuSO4 and antioxidant, NAC (N-acetyl-L-cysteine, Sigma). Plates were photographed after 4 days of incubation at 30°C. (b) NAC reduces lethality due to TDP-43. An integrant of CUP1-TDP-43-YFP (TDP-43) with high toxicity and vector (control) grown on synthetic dextrose medium without CuSO4 were inoculated to OD600 = 0.5 in dextrose medium with (+) or without (−) 250 μM CuSO4 and 0 mM or 1 mM NAC. After 24 h growth cells were stained with trypan blue to identify dead cells5 and counted. (c) NAC reduces TDP-43-YFP level. Cells from (b) were photographed with bright field (left), fluorescence and bright field (middle) and just fluorescence (right). TDP-43-YFP fluorescence was barely observed in NAC treated cells even at the very high exposure shown. Black cells indicate trypan blue stained dead cells.
