FIGURE 1.
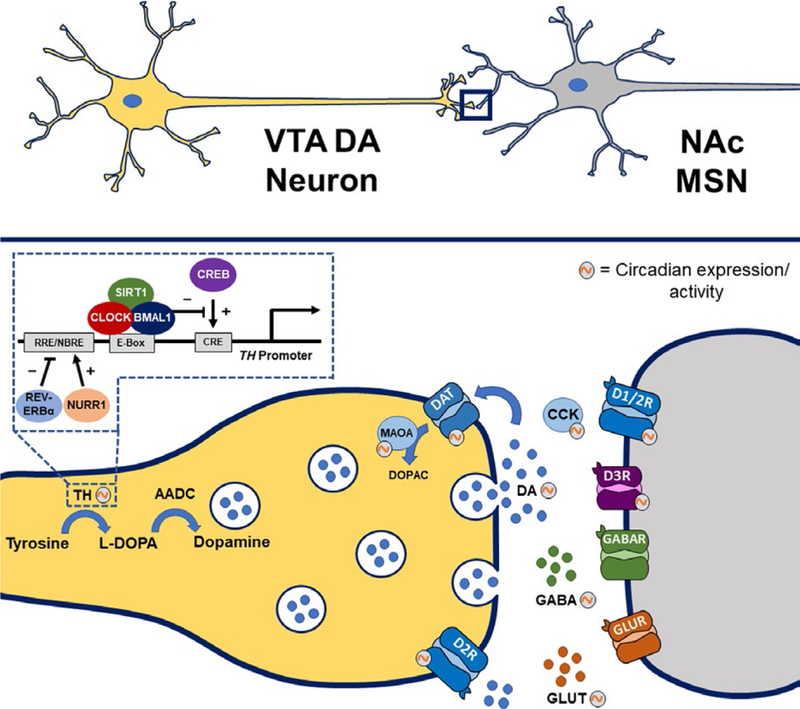
Clock genes regulate components of dopaminergic transmission within the ventral tegmental area (VTA)-nucleus accumbens (NAc) circuitry. Components of the dopamine synapse involved in the synthesis, uptake, and degradation of dopamine show circadian rhythms in expression or activity. These rhythmic components include tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), monoamine oxidase A (MAOA), dopamine transporter (DAT), and dopamine receptors type 1 (D1R), type 2 (D2R), and type 3 (D3R). Tyrosine hydroxylase transcription is activated by cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB)-mediated binding to CRE sites in the TH promoter. The CLOCK/BMAL1 complex interacts with the histone and protein deacetylase, Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1), to repress CREB-induced TH transcription in a diurnal-dependent manner. There are also circadian rhythms in various neurotransmitters and neuropeptides, including dopamine (DA), glutamate (GLUT), γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), and cholecystokinin (CCK)
