FIGURE 3.
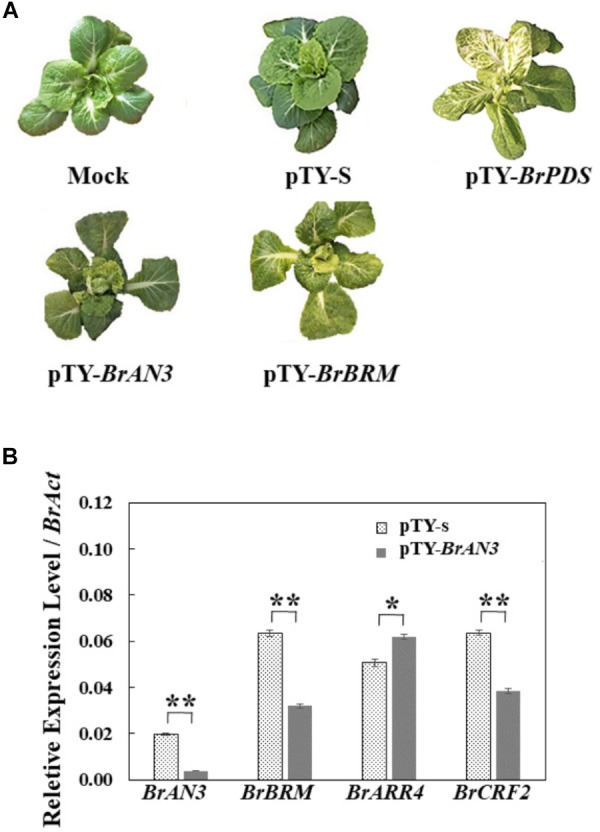
Effects of gene silencing of BrAN3 and BrBRM in Chinese cabbage. (A) Representative images of the silencing plants by using the TYMV-derived vector pTY-S at 60 DPI. A gene-specific fragment of 40 nt in length was selected for each of the two genes to create an in-frame stop codon (TAA, TGA, or TAG) on the second, third or fourth amino acid position on each fragment due to frame shift. The gene-specific fragment was selected to target all the homologous sequences of each gene in the Chinese cabbage genome. Six weeks old Chinese cabbage plants were inoculated with each gene silencing vector. The mock treatment and the empty vector pTY-S were used as the negative control, while the pTY-BrPDS was used as the positive control. Leaf head formation was observed for pTY-BrAN3 and pTY-BrBRM-inoculated plants. (B) Relative expression levels of BrAN3, BrBRM, and two of BrAN3 downstream genes BrARR4 and BrCRF2 in the BrAN3-silencing plants measured by Real-time RT-PCR. RNA was extracted from the BrAN3-silencing leaves with the empty vector pTY-S-inoculated leaves as the control at 60 DPI. Relative expression levels were calculated using the standard curve method with BrAct (Bra028615; Dheda et al., 2004) as the internal control gene. Bars represent the means of three replicates ± standard errors (vertical bars). Asterisks indicate a significant difference between the two stages at p ≤ 0.05 as calculated by t-test.
