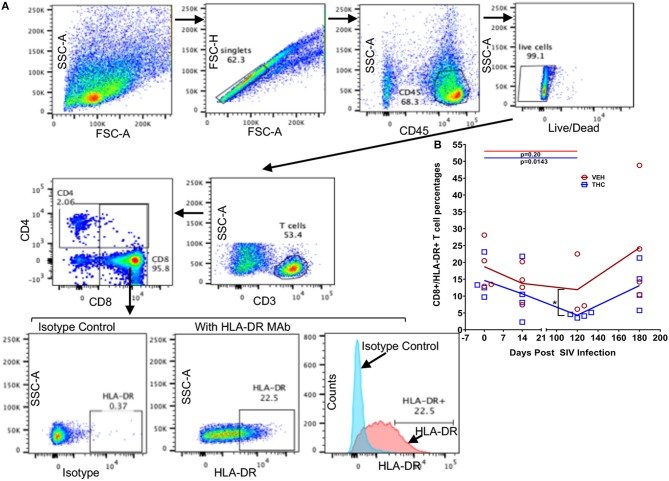
Figure 9.
Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) administration inhibited HLA-DR expression in intestinal CD8+ T cells after SIV infection. Gating strategy for HLA-DR expression from a representative VEH/SIV rhesus macaque (A). Cells were gated first on singlets, CD45 (lymphocyte common antigen), followed by live cells, and then on CD3+ T cells. T-cells were further gated on CD3+CD4+ and CD3+CD8+ T cell subsets. The percentages of total HLA-DR expression in CD8+ T cells are shown in the bottom row where the positive HLA-DR expression was compared to the isotype control both in the dot plots and histograms. (B) THC/SIV rhesus macaques showed reduced percentage of CD8+ T cells expressing the late activation marker HLA-DR at 120 days post SIV compared to VEH/SIV rhesus macaques. Note that data from only three VEH/SIV rhesus macaques were available for the 120 days post-infection time point as LPL yields from one animal were insufficient for flow cytometry. Open red circles- VEH/SIV, Open blue squares- THC/SIV. Horizontal red and blue lines with P-values denote comparisons between time points within the VEH/SIV and THC/SIV groups, respectively. Left black brackets with an asterisk indicate statistical significance (p = 0.0286) between the VEH/SIV and THC/SIV groups for a given time point. Connecting blue and red lines (B) denote mean values of the respective population in the THC/SIV and VEH/SIV groups, respectively. Flow cytometry analysis to determine the effect of Δ9-THC on HLA-DR expression in intestinal CD8+ T cells of SIV-infected rhesus macaques was performed once with three to four individual animals as biological replicates per group. Flow cytometry data were analyzed using linear mixed models with immune-marker outcomes being dependent variables, and treatment status (VEH vs. Δ9-THC) and days since the start of treatment (0, 14, 120, 180) being independent variables with fixed effects. Differences between two time points were analyzed using the Mann-Whitney U-test employing the Prism v5 software (GraphPad software). A p-value of ≤0.05 was considered significant.