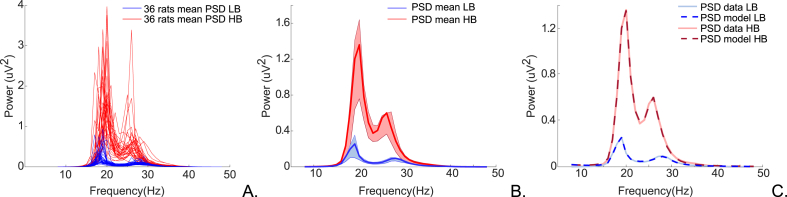
Fig. 4.
Observed and expected power spectral densities (PSD). (A) Spectral features to be explained by a DCM: Red lines depict the mean high beta spectral densities and blue lines the mean low beta spectral densities from each of the 36 rats. (B) Group mean of HB spectral densities in red and LB spectral densities in blue. Respective variabilities (75th and 25th percentiles of the mean spectra) denoted in light red and light blue. (C) Goodness of the fits between mean data spectral densities and spectral densities generated by the winning model. The full red line shows the mean of high beta data and the dark red dashed line the high beta spectra estimated by the winning model (correlation coefficient, r = 0.9997). The full dark blue line refers to the mean of low beta data and the dark blue dashed line to the low beta spectra produced by the winning model (correlation coefficient, r = 0.9957).