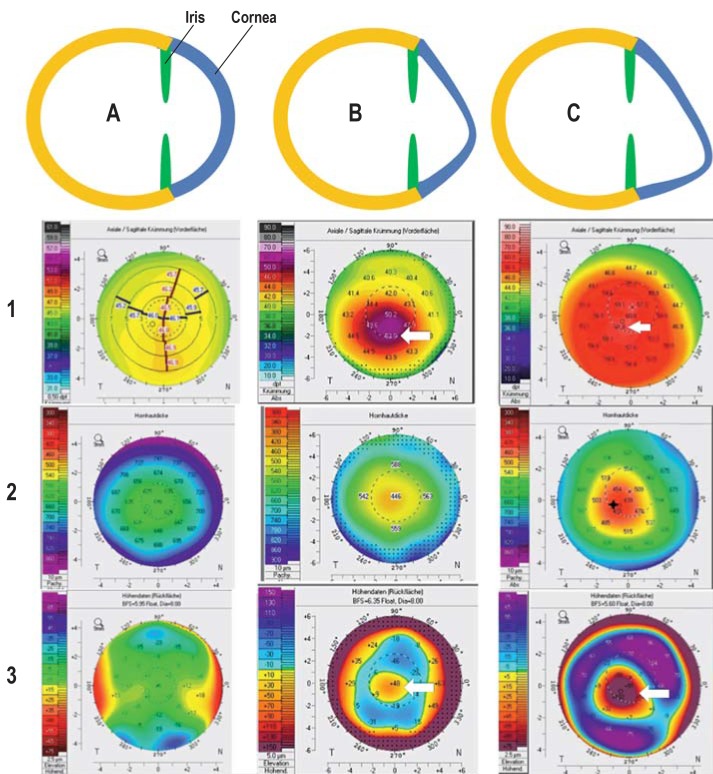
Figure 1.
Progressive disease course in keratoconus as a schematic representation with examples of tomographic findings
A: Normal corneal shape; unremarkable tomography with evenly distributed anterior corneal refractive power (1), corneal thickness (2), and curvature of the posterior corneal surface (3)
B: Early-stage keratoconus with marked deformation in a downward direction (increase in refractive power on the anterior corneal surface up to 52 diopters [1, arrow] and “island-shaped” protrusion of the posterior corneal surface [3, arrow]) and corneal thinning to 446 µm (2)
C: Late-stage keratoconus with marked deformation in a downward direction (increase in refractive power on the anterior corneal surface up to 61.8 diopters [1, arrow] and “island-shaped” protrusion of the posterior corneal surface [3, arrow]) and corneal thinning to 429 µm (2)
Figure: Archives of the Eye Center at the University of Freiburg Medical Center, Germany