Fig. 1.
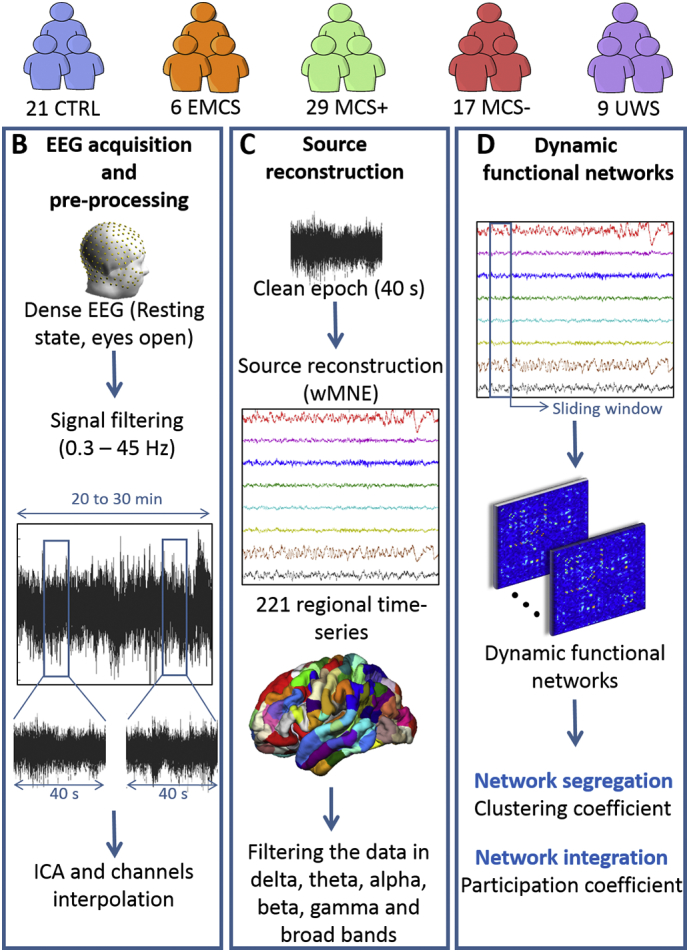
Data processing pipeline. (A) Database: Patients were diagnosed according to repeated assessments with the CRS-R into EMCS, MCS+, MCS- and UWS. The demographic details are listed in Supplementary Table T1. (B) EEG acquisition and preprocessing: High-density-EEGs were recorded using 256 electrodes during resting-state (eyes open, in the dark) for 20 to 30 min. Signals were then filtered between 0.3 and 45 Hz and segmented into 40 s epochs. Independent Component Analysis (ICA) was applied and bad channels were interpolated. Finally, the first five clean epochs were kept for analysis. (C) Source reconstruction: EEG cortical sources were estimated using the weighted norm estimation method (wMNE). This step was followed by a projection of the source signals on an atlas based on Desikan-killiany and Hagmann atlases, using a template brain. Reconstructed regional time series were filtered in six different frequency bands: Delta (1–3 Hz), Theta (3–7 Hz), Alpha (7–13 Hz), Beta (14–25 Hz), Gamma (30–45 Hz) and Broadband (1–45 Hz). (D) Dynamic functional networks: Functional connectivity matrices were computed using the phase locking value (PLV) calculated using a sliding window technique. Networks were then characterized by their clustering coefficient (segregation) and participation coefficient (integration).
