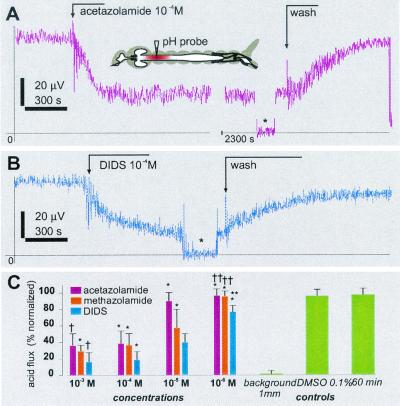
Figure 4.
Pharmacological effects of acetazolamide, methazolamide, and DIDS on acid efflux in the anterior midgut of mosquito larvae. (A and B) Time course of SERIS-pH-LIX probe readings during basal application of acetazolamide (A) and DIDS (B). Broken arrows indicate events during recording. *, A background signal at 1 mm from the tissue. (Inset) The approximate position of the recording probe. (C) Normalized dose–response histogram of acid efflux inhibition. Bars are mean ± SD (n ≥ 4 for each concentration). *, A significant difference of the value compared with a value from the preceding 1:10 dilution (paired t test, P > 0.001 for all significant definitions); †, insignificant differences of the value compared with the value from the preceding 1:10 dilution; **, significant differences compared with 0.1% DMSO and 30-min controls; ††, insignificant difference compared with the controls.