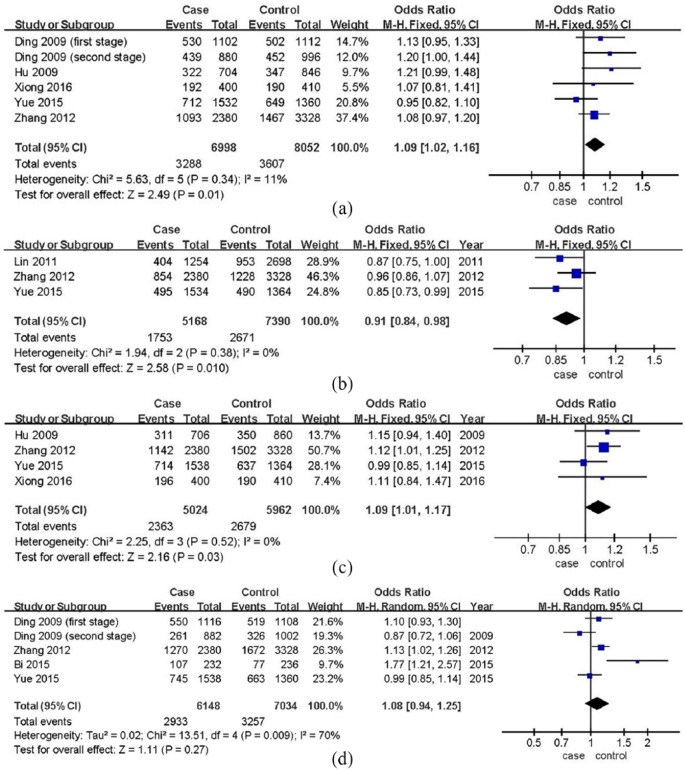
Figure 2.
displayed the additive models (comparisons of alleles). Since Ding et al.6 was a two-stage study, we divided it into two studies in comparisons of rs2383206 and rs10757278. No significant heterogeneity was identified in allele comparisons of rs2383206, rs2383207, and rs10757274 (I2 < 50%), so fixed-effects models were applied. For rs10757278, a random-effects model was used (I2 > 50%). Polymorphisms of rs2383206 and rs10757274 were significantly associated with IS risk, and allele G increased the risks (allele G was mutant type). In addition, a mutant from allele G to A of rs2383207 could protect subjects from IS. No statistical association was identified in allele comparison of rs10757278: (a) allele comparison of rs2383206 (G versus A), (b) allele comparison of rs2383207 (A versus G), (c) allele comparison of rs10757274 (G versus A), and (d) allele comparison of rs10757278 (G versus A).