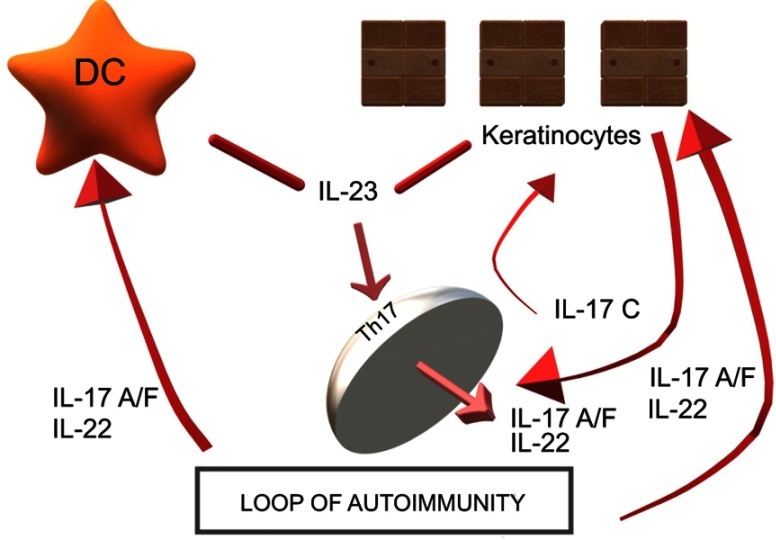
Figure 1.
IL-17A and IL-17C are involved in a mutual relationship wherein IL-17A strongly induces IL-17C in keratinocytes and IL-17C is capable of synthesizing IL-17A in T lymphocytes. IL-17C may also play a role in other skin inflammatory diseases; inhibiting IL-17C may therefore be beneficial in both psoriasis and AD patients: antibody-dependent blockade of IL-17C inhibited cutaneous inflammation in the IL-23-induced psoriasis model and even in AD-like inflammation in mice.
Abbreviations: AD, atopic dermatitis; DC, dendritic cell; IL, interleukin; Th, lymphocyte T helper.