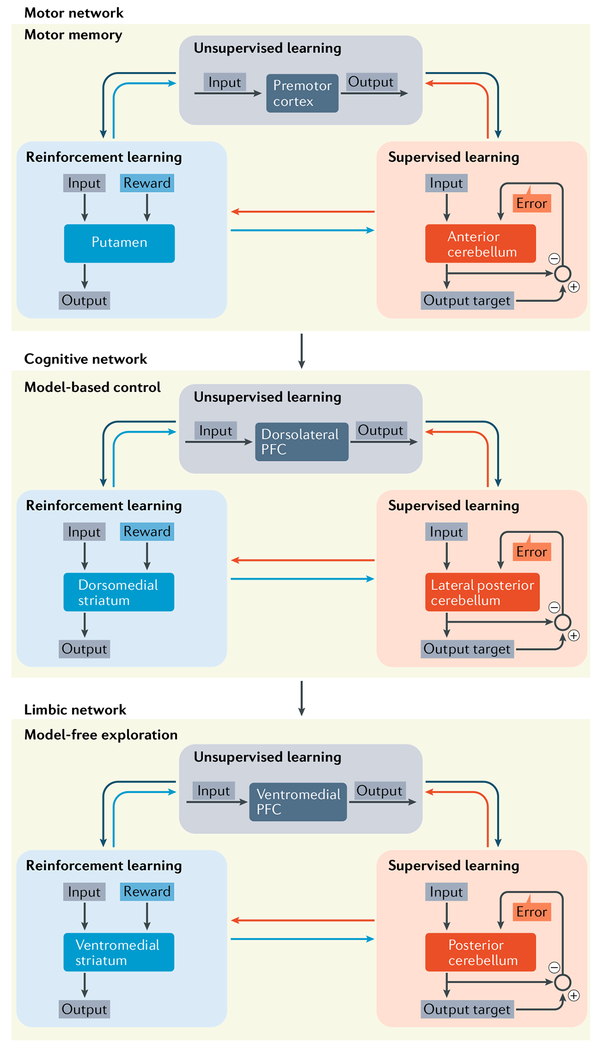
Fig. 6 |. Action planning.
Functionally related corticai, basal ganglia and cerebellar sites within interconnected networks participate in progressive stages of action planning123. On the basis of these results, learning through exploration involves a limbic network, including the ventromedial prefrontal cortex (PFC), ventromedial striatum and posterior cerebellum. Model-based learning involves an associative (cognitive) network, including the dorsolateral PFC, dorsomedial striatum and lateral posterior cerebellum. Performance based on motor memory involves a motor network , including the supplementary motor area, putamen and anterior cerebellum. The authors’ imaging data suggest that as learning progresses, the sites of activation shift in a topographically organized fashion. Our interpretation of these data is that each stage of the learning progress involves a different set of interconnected basal ganglia, cerebellar and cerebral cortical regions.