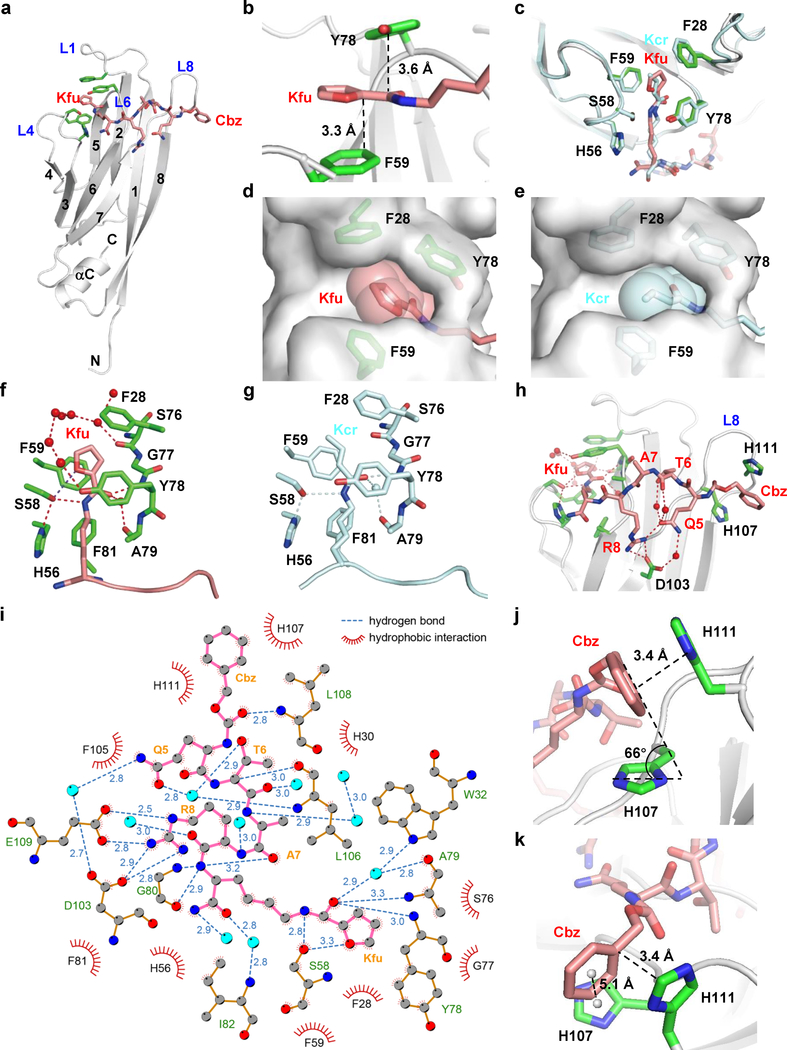
Figure 3. Molecular basis underlying AF9 YEATS and XL-07i interaction.
(a) Overall structure of AF9 YEATS bound to XL-07i in ribbon view. (b) The π system of XL-07i forms the expected π-π-π stacking with F59 and Y78 of AF9. (c) Superimposition of the aromatic ‘sandwich’ cage in XL-07i-bound AF9 YEATS with H3K9cr-bound AF9 YEATS. (d-e) Comparison of cavity encapsulation of (d) Kfu and (e) Kcr shown in surface view. (f-g) Hydrogen bonding networks in the binding pockets with (f) Kfu and (g) Kcr. (h) Detailed hydrogen-bonding interaction network between AF9 YEATS and XL-07i. (i) LIGPLOT diagram illustrating the contacts between XL-07i and the AF9 YEATS domain. XL-07i (pink) and key residues of AF9 YEATS (gold) are depicted in ball-and-stick mode. Grey ball, carbon; blue ball, nitrogen; red ball, oxygen; cyan ball, water molecule. Numbers showing the distance of indicated hydrogen bonds in Å. (j-k) The Cbz of XL-07i forms parallel-displaced and edge-to-face π stacking with H107 and H111 of AF9 YEATS in loop L8, respectively. For AF9 YEATS-XL-07i complex structure, AF9 YEATS (grey) is shown as ribbons, key pocket residues (green) and the XL-07i (salmon) are depicted as sticks; hydrogen bonds are shown as red dashes; the water molecules are represented as red balls; the centroids of aromatic rings are represented as grey balls. For AF9 YEATS-H3K9cr complex structure, AF9 YEATS, hydrogen bonds, and water molecules are colored and labeled cyan. Kfu: 2-furancarbonyl lysine.